 INFRA
INFRA
 INFRA
INFRA
 INFRA
INFRA
The Open Network Foundation has announced a new development framework that aims to advance software-defined networks and network virtualization through open-source platforms, network device disaggregation and new network standards.
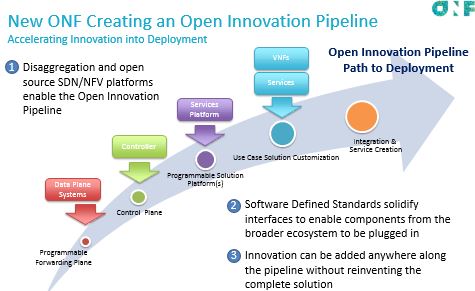
The new initiative is called the Open Innovation Pipeline, which builds on earlier efforts to leverage SDN and network function virtualization, which aim to make networking more directly programmable, by “industrializing” development processes used to build open network platforms. Those previous efforts include the CORD initiative, which stands for “Central Office Re-architected as a Datacenter,” and the Open Network Operating System.
The foundation, which is in the process of merging with the similarly SDN-focused Open Networking Lab, says its current method is to work with network operators to build frameworks based on “high-value use cases.” Those architectures are then pushed through to prototypes, trials and finally, deployment. With the new initiative, the ONF and its partners want to deploy open network platforms that are based on the separation of control software and networking devices.
“The industry needs a unifying effort to build solutions out of the numerous disaggregated components,” the ONF said in its pitch.
Guru Parulkar, executive director of the ONF, said the pipeline would allow members from various industry segments to bring unique innovation and value to an open networking solution. “Operators, vendors and integrators all have a role to play, and the pipeline helps integrate these contributions into consumable solutions for operators,” he added.
Proponents claim that an open networking approach benefits network operators, integrators and vendors alike. For carriers in particular, the ONF says that SDN and NFV will deliver “cloud-like DevOps efficiencies to the carrier network,” while there’s also an opportunity for system integrators due to pent up demand for network modernization, which has created a big skills gap for operators.
The ONF is backed by a number of major players in the telecommunications industry, including AT&T Inc., NTT Communications Inc. and SK Telecom Co., Ltd., as well as Google Inc.
“The networking space has been slowest to offer end-to-end open source alternatives,” said Urs Hölzle, ONF chairman and Google’s senior vice president for technical infrastructure. “SDN is a chance to rearchitect how networks are built, and while so doing, presents the perfect inflection point for open source to take on a pivotal role.”
News of the latest initiative comes just weeks after ONF member AT&T said it was open-sourcing a solution for automating network virtualization. The ECOMP (enhanced control, orchestration, management and policy) framework is designed to facilitate policy-driven software automation of virtual network functions in real time. It leverages cloud technologies along with network virtualization to offer new network services, and can handle diverse workloads, ranging from the real-time creation of virtual machines on commercial hardware to the dynamic assignment of applications and workloads, AT&T said.
The ONF said that it hopes its merger with the Open Networking Lab should be completed by the end of the year.
Support our mission to keep content open and free by engaging with theCUBE community. Join theCUBE’s Alumni Trust Network, where technology leaders connect, share intelligence and create opportunities.
Founded by tech visionaries John Furrier and Dave Vellante, SiliconANGLE Media has built a dynamic ecosystem of industry-leading digital media brands that reach 15+ million elite tech professionals. Our new proprietary theCUBE AI Video Cloud is breaking ground in audience interaction, leveraging theCUBEai.com neural network to help technology companies make data-driven decisions and stay at the forefront of industry conversations.