 CLOUD
CLOUD
 CLOUD
CLOUD
 CLOUD
CLOUD
Google LLC today announced updates to its hybrid cloud management platform Anthos to bring more enterprise-ready capabilities aimed at enhancing security for microservices and governing workloads across the cloud.
The tech giant launched Anthos as a rebranding of its Cloud Services Platform in April. The platform is described as a modern application management environment designed to provide a consistent experience for development and operations between both cloud and on-premises data centers.
That means applications developed for Anthos will run similarly no matter where they are deployed and managed, taking tension off developers who must worry about different tools and deployment standards depending on where an application is running.
The announcement today includes two brand new capabilities for Anthos: Service Mesh, a connector for managing microservices, and Cloud Run, a platform that enables seamless runs for stateless workloads in a fully managed cloud environment.
Microservices are an application design framework where individual activities that make up an app are split apart into their own environments — such as the ability to look up the identity and authorization of a user might be part of a bigger application. Breaking a big application down into microservices increases complexity considerably, and, as a result, the need for highly capable management.
Anthos Service Mesh provides this management experience by delivering an abstraction layer with a uniform way to connect, secure, monitor and manage those microservices. It uses a “service mesh” or a network of virtual machine processes as high-performance and lightweight proxies to manage the underlying needs of those services. The idea is to maintain communication, provide enhanced security and give better visibility into operations.
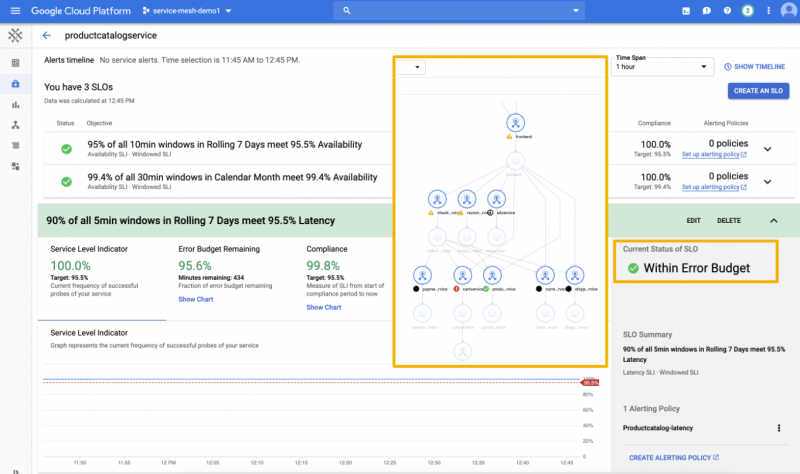
Image: Google
As a mesh, all communications among proxies by microservices is also monitored. That means development and operations staff can get deep visibility into the traffic within and between applications. In turn that gives developers valuable insights into potential bottlenecks and miscommunication. As a result, Anthos can make it much easier to troubleshoot misbehaving applications.
Cloud Run for Anthos gives developers a way to escape from centralized servers when running applications with an environment known as “serverless computing,” which is the underlying aim of much of cloud computing. It allows for the ability to run workloads without having to worry about underlying infrastructure.
Currently in beta, Cloud Run is based on Knative, an open application programming interface and runtime environment for services that run on cloud-based serverless environment Kubernetes.
With Cloud Run, developers write code exactly as if they were writing for any other environment with no need to learn advanced Kubernetes concepts. The platform itself takes care of the heavy lifting by tuning code to run on serverless cloud environments and handles the interapplication communication and security.
The environment enforces best practices, provides access to custom machine types, offers advanced networking support and enables cloud accelerators. That means workloads can all run in the same cluster, which speeds up communication among components considerably. It also means everything is in one place when operations staff need to get a better understanding of what’s happening under the hood — that is, there’s only one hood to lift.
According to Google, Cloud Run can flexibly run workloads — by providing a scalability from zero to many virtual machines — on Google Cloud or on-premise with the same consistent experience.
“Google continues to build on it’s offering with a focus on solutions that leverage open source and emphasize hybrid and multi-cloud,” Stu Miniman, senior analyst at Wikibon. “While Google creates impressive technology, and they have the flexibility of supporting virtual machines, containers, and serverless, customers may struggle to understand how to leverage these offerings to accelerate their digital transformation.”
In addition, Google announced a new development-centric security check system called Binary Authorization. With this system, defined security checks can be baked in earlier in the development process to make sure that only trusted workloads are deployed in test and live environments. This is done by assuring that workloads are assessed and validated before they are deployed. As a result, enterprises can be confident that workloads can be trusted.
One final announcement is the addition of a policy controller and config connector called Anthos Config Management. With this system, development and operations can enforce consistent security policies and controls continuously across cloud environments. This includes Google Cloud, on-premises and even other clouds.
Google considers Anthos to be the best-in-class cloud application environment for the enterprise cloud with comprehensive capabilities covering container management, service mesh, security, monitoring and logging. The service is expected to be a huge benefit to enterprise users seeking to modernize on the path to the cloud while continuing to use the configuration and pace that works for the organization.
THANK YOU