 CLOUD
CLOUD
 CLOUD
CLOUD
 CLOUD
CLOUD
Google LLC today is rolling out a new “carbon-intelligent computing platform” for its data centers.
The technology is designed to shift the timing of certain kinds of compute tasks so as to maximize how its facilities use renewable energy from low-carbon power sources such as wind and solar. Google said that by shifting the timing of non-urgent compute tasks, such as creating new filters for Google Photos, processing videos in YouTube and adding new words to Google Translate, it can significantly reduce its carbon footprint.
The launch of the new platform coincides with Earth Day, which is an annual event celebrated around the world on April 22 to demonstrate support for environment protection.
Google has already made progress in its bid to become more sustainable. It has been carbon neutral since 2007, and in 2019 it matched its energy usage with 100% renewable energy purchases for the third year in a row.
“Now, we’re working toward 24×7 carbon-free energy everywhere we have data centers, which deliver our products to billions of people around the world,” Google said in a blog post. “To achieve 24×7 carbon-free energy, our data centers need to work more closely with carbon-free energy sources like solar and wind.”
That’s why Google’s new carbon-intelligent computing platform should come in handy. The platform works by comparing two kinds of forecasts for each day. The first forecast predicts how the average hourly carbon intensity of the local electrical grid will change over the course of a day.
Meanwhile, a second forecast predicts how many power resources will be needed by each of its data centers to carry out their compute tasks during the same 24-hour period. Those forecasts are then used to schedule all nonessential compute tasks for times when more low-carbon energy resources are available, Google said.
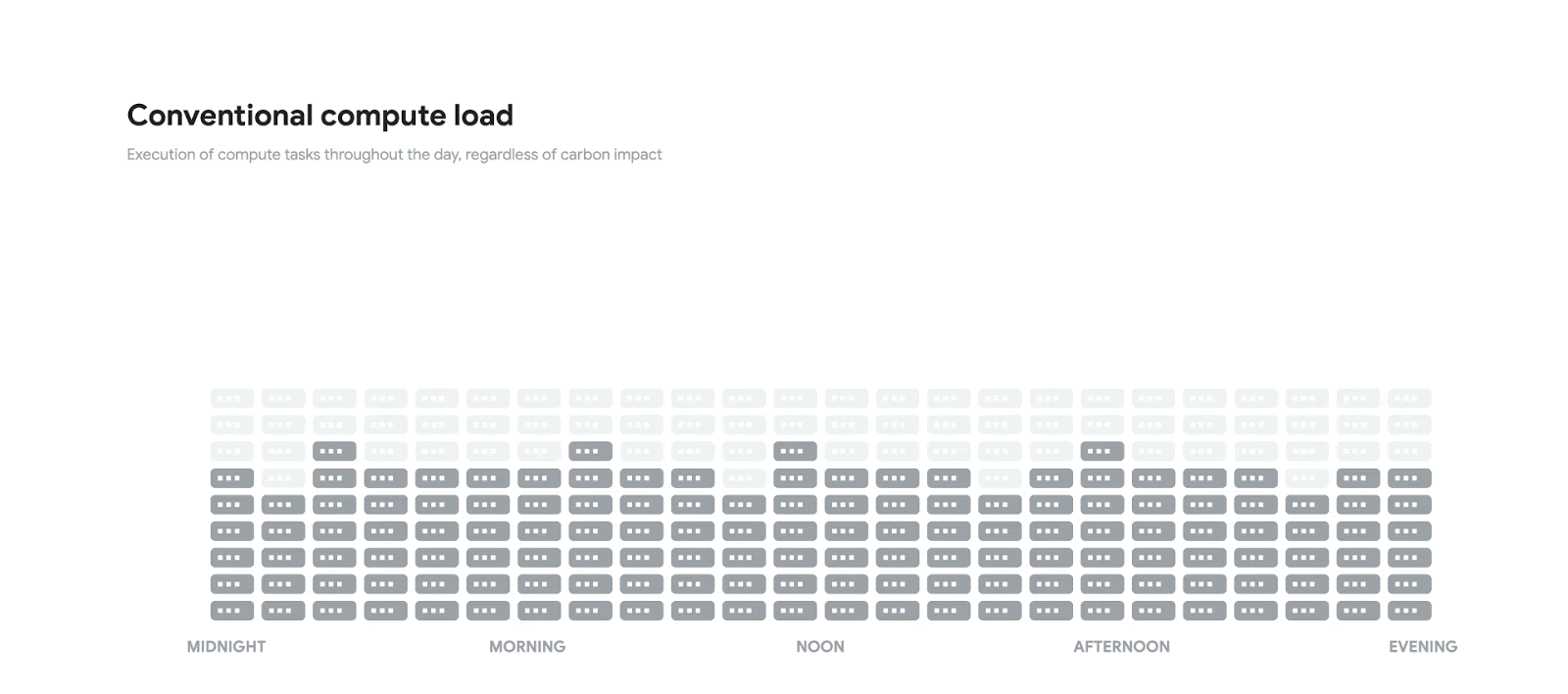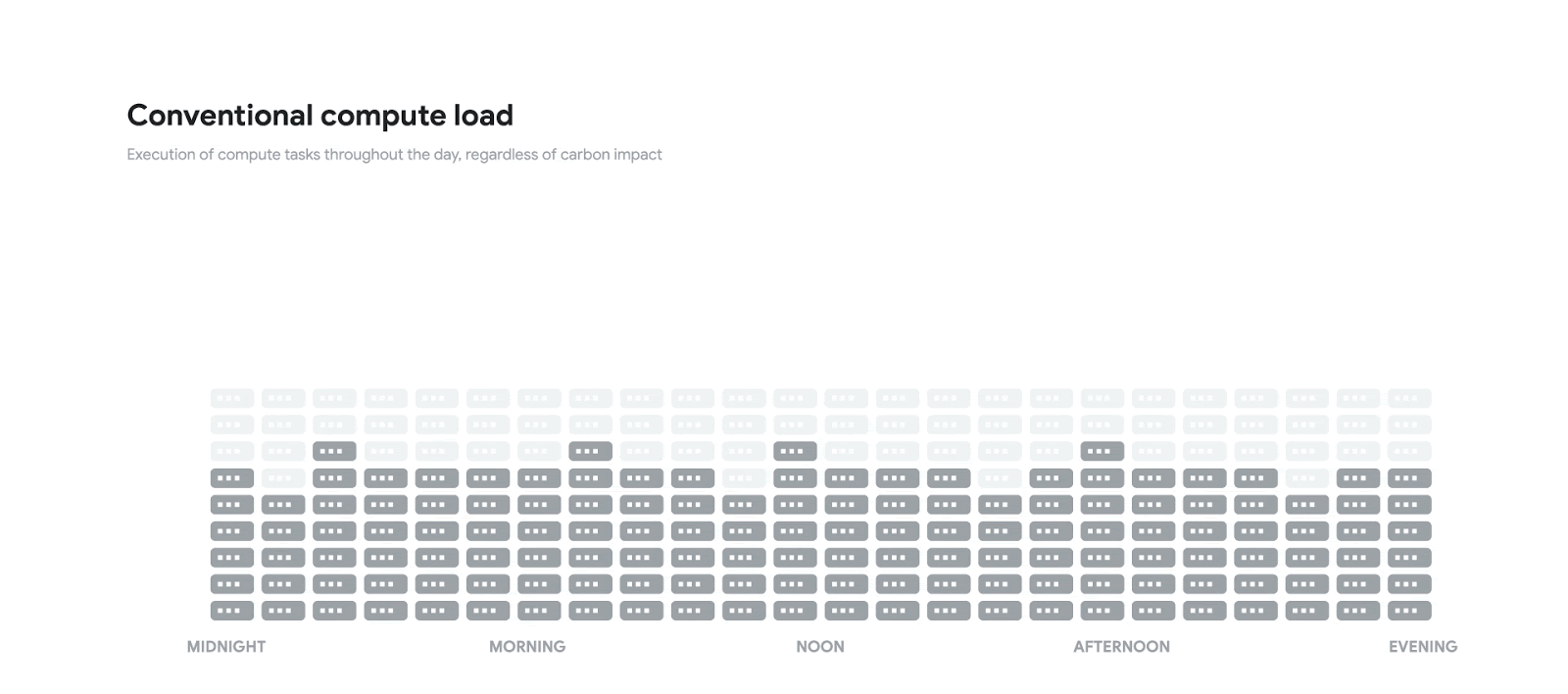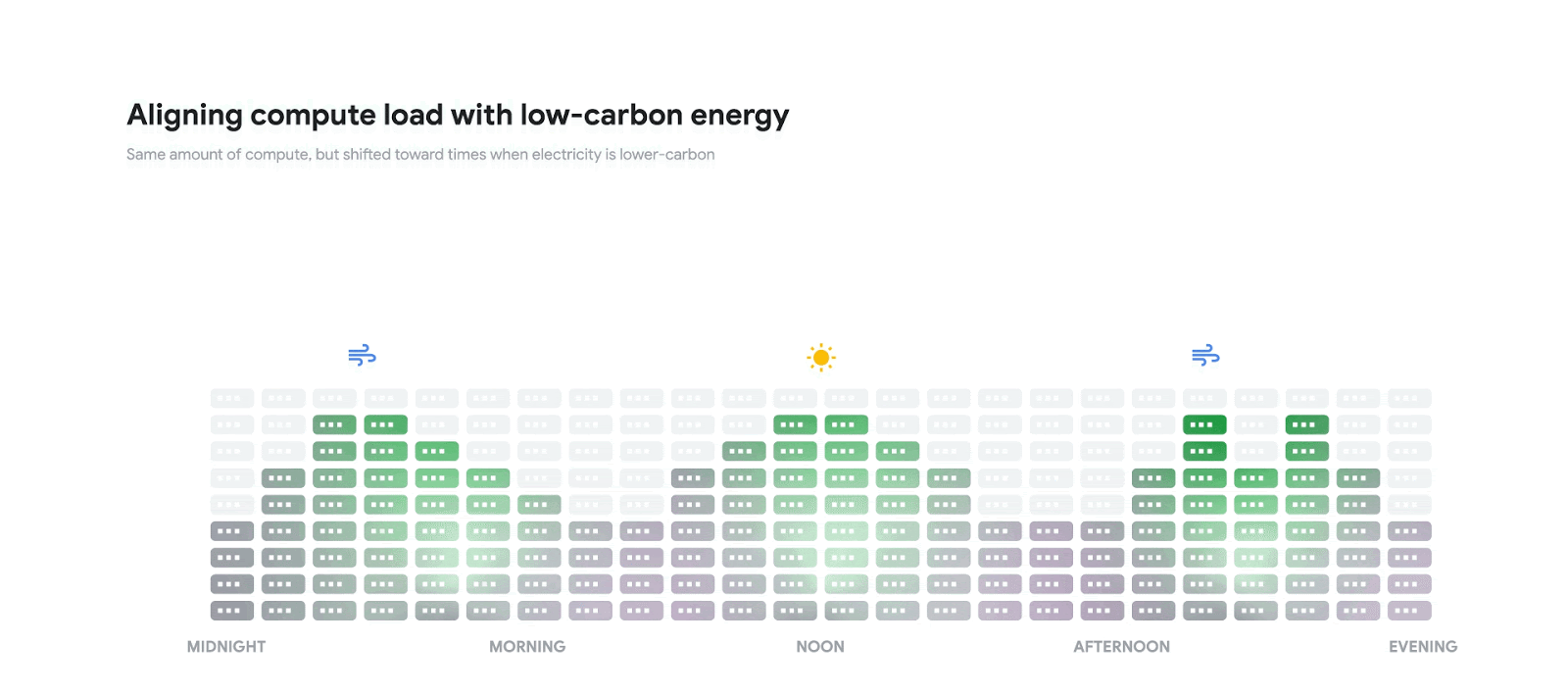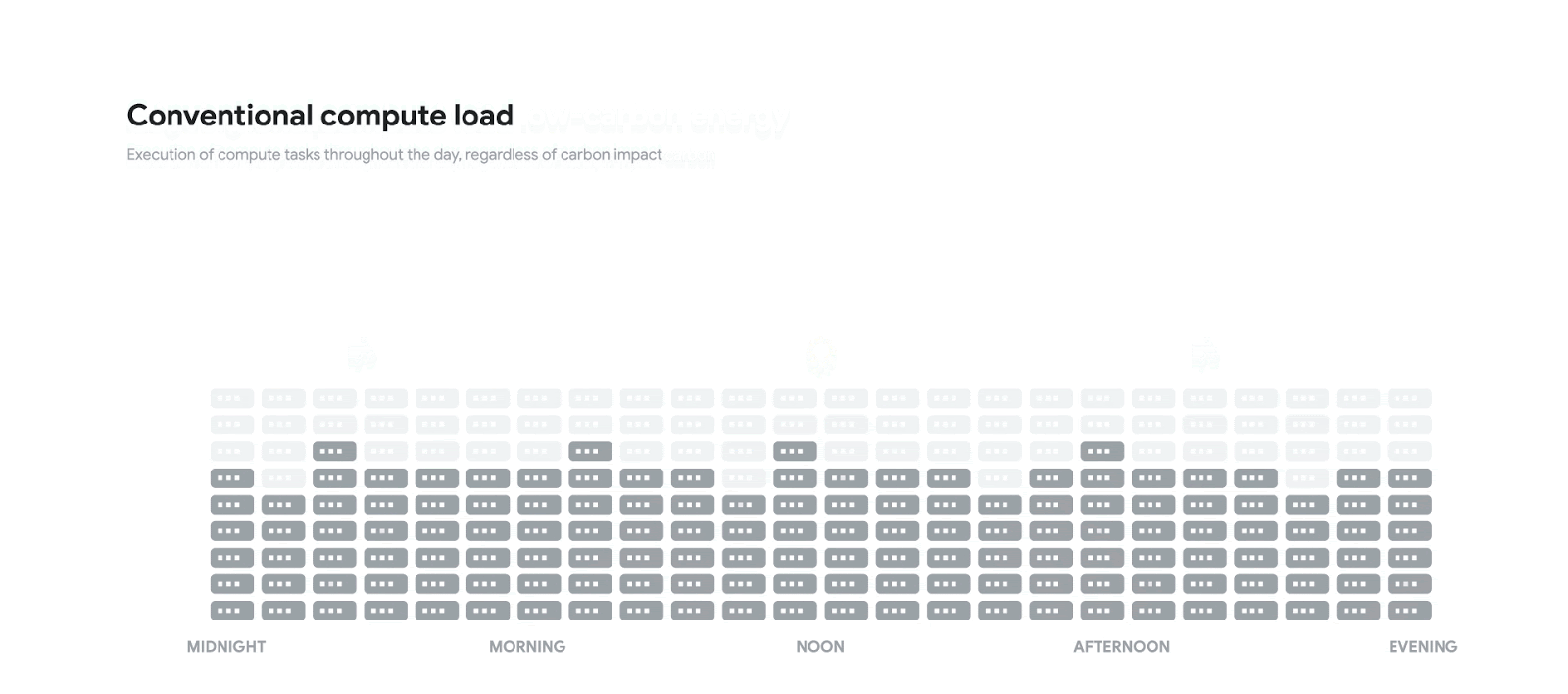
“Early results demonstrate carbon-aware load shifting works,” Google wrote. “Results from our pilot suggest that by shifting compute jobs we can increase the amount of lower-carbon energy we consume.”
At present, the platform only works by shifting compute tasks to different times of the day, within the same data center. But in future Google believes the platform will be far more flexible, able to shift tasks among different data centers so more work can be done when environmentally friendly resources are available.
“Our plan for the future is to shift load in both time and location to maximize the reduction in grid-level CO2 emissions,” Google said. “Our methodology, including performance results of our global rollout, will be shared in upcoming research publications. We hope that our findings inspire other organizations to deploy their own versions of a carbon-intelligent platform.”
Support our mission to keep content open and free by engaging with theCUBE community. Join theCUBE’s Alumni Trust Network, where technology leaders connect, share intelligence and create opportunities.
Founded by tech visionaries John Furrier and Dave Vellante, SiliconANGLE Media has built a dynamic ecosystem of industry-leading digital media brands that reach 15+ million elite tech professionals. Our new proprietary theCUBE AI Video Cloud is breaking ground in audience interaction, leveraging theCUBEai.com neural network to help technology companies make data-driven decisions and stay at the forefront of industry conversations.