 AI
AI
 AI
AI
 AI
AI
Meta Platforms Inc. is looking to promote the responsible development of artificial intelligence systems with a new initiative called Purple Llama.
Announced today, it’s a project that Meta says will slowly make available all of the tools and evaluations the AI development community needs to build open generative AI models in a safe and responsible way.
In a blog post, Meta’s AI research team explains that generative AI is powering a wave of innovation, with conversational chatbots, image generators, document summarization tools and more now being widely used across the world. Many of these new generative AI applications are powered by Meta’s open-source Llama large language models.
As such, Meta feels compelled to take responsibility and encourage collaboration on AI safety, saying this is necessary to build trust in these new innovations. “The people building AI systems cannot address the challenges of AI in a vacuum, which is why we want to level the playing field and create a center of mass for open trust and safety,” the company explained.
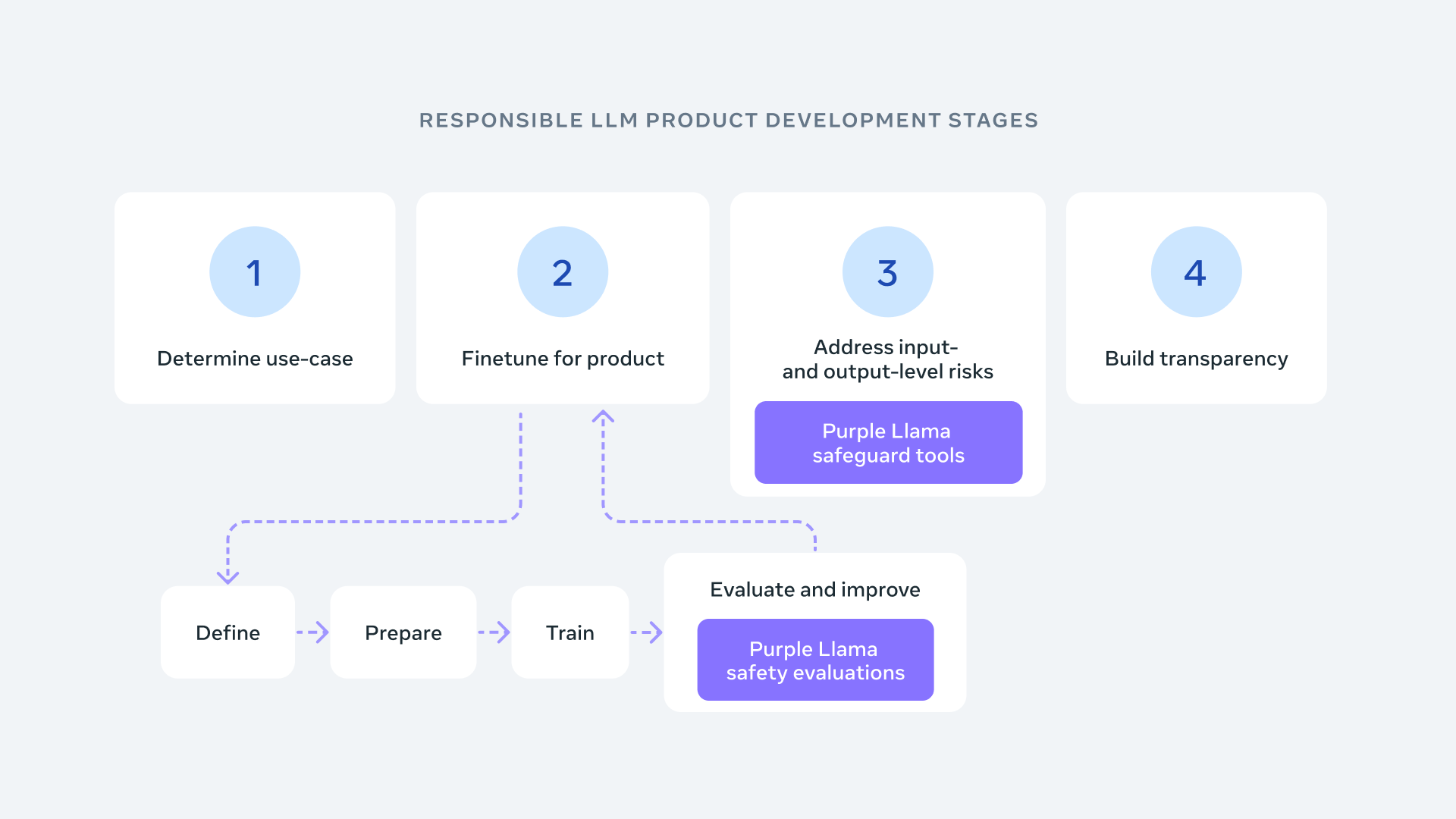
To get things started, Meta is kicking off Purple Llama with the release of a free and open set of cybersecurity evaluation benchmarks for LLMs, called CyberSec Eval. It’s also announcing Llama Guard, which is a safety classifier for input/output filtering that has been optimized for easy deployment.
In a blog post, Meta says cybersecurity and LLM prompt safety are two of the most important areas in generative AI safety, as highlighted within its Llama 2 Responsible Use guidelines.
CyberSec Eval is believed to be the first industrywide set of cybersecurity safety evaluations for LLMs. The benchmarks are based on industry standards and guidance, and were developed in collaboration with security subject matter experts, Meta said.
They provide metrics for developers to quantify LLM security risks, and they’re designed to address issues such as the frequency of insecure code suggestions. They also enable developers to evaluate LLMs to make it more difficult for applications to generate malicious code that could be used to aid in cyberattacks.
Meta said the new tools will help to prevent hackers and other malicious actors from using LLMs to facilitate cyberattacks. Its earlier research has unearthed what it says are “meaningful risks” that generative AI can be used to generate insecure code and comply with malicious requests.
As for Llama Guard, it’s a pretrained model that’s designed to prevent generative AI models from generating potentially risky outputs, Meta said. It was trained on a mix of publicly available datasets to enable it to detect common kinds of risky or violating content that may be relevant to many different kinds of use cases. So it can detect both risky prompts and outputs from generative AI models, and prevent them from being processed. Ultimately, Meta said, this will help developers to customize their generative AI models to support relevant use cases, while minimizing the risk of causing controversy, upset or offense.
Meta said Purple Llama is an appropriate name for its new AI safety initiative because mitigating the risks of generative AI requires developers to combine attack, in the shape of “red teaming,” and defense, through so-called “blue teaming.” In traditional cybersecurity, red teams consist of experts who carry out various attacks to try and overcome a company’s cybersecurity defenses, while the blue teams are focused on protecting and responding to those attacks.
Therefore, Meta is labeling its approach to generative AI security as “purple teaming,” with an aim to foster a collaborative approach to evaluating and mitigating the potential risks of the technology.
As part of the Purple Llama initiative, Meta intends to carry out tons of exploratory research, but it won’t do it alone. Rather, it’s creating an open ecosystem, with partners including the newly announced AI Alliance, Advanced Micro Devices Inc., Anyscale Inc., Amazon Web Services Inc., Bain & Company, CloudFlare Inc., Databricks Inc., Dell Technologies Inc., Dropbox Inc., Google Cloud, Hugging Face Inc., IBM Corp., Intel Corp., Microsoft Corp., MLCmmons, Nvidia Corp., Oracle Corp., Scale AI Inc., Together Computing Inc. and many others.
The announcement of today’s initiative comes hot on the heels of Meta joining IBM Corp.’s AI Alliance, and appears to be one of the first steps towards meeting the goals of the latter organization, said Andy Thurai, vice president and principal analyst of Constellation Research Inc. “Meta has taken a first step in releasing a set of tools and frameworks ahead of the work produced by the committee even before the team is finalized,” the analyst pointed out.
Thurai added that it’s worth mentioning that Meta is working with a number of companies that notably have not joined the AI Alliance, including AWS, Google, Microsoft and Nvidia, which are some of the industry’s biggest players.
“Meta is planning to license them both commercially and for research which was the biggest gripe about the LLaMa model licensing option restrictions,” Thurai added. “The proposed tool set is supposed to help LLM producers with metrics about LLM security risks, insecure code output evaluation, and/or potentially limit the output from aiding bad actors to use these open source LLMs for malicious purposes for cyberattacks. It’s a good first step, and I would like to see a lot more.”
The Purple Llama project’s components, including CyberSec Eval and Llama Guard, will be licensed on a permissive basis that allows for both research and commercial use. Meta said it will showcase the first of these components at the NeurIPs 2023 event that kicks off on Dec. 10, where it will provide a technical deep dive for developers wanting to implement them.
Support our mission to keep content open and free by engaging with theCUBE community. Join theCUBE’s Alumni Trust Network, where technology leaders connect, share intelligence and create opportunities.
Founded by tech visionaries John Furrier and Dave Vellante, SiliconANGLE Media has built a dynamic ecosystem of industry-leading digital media brands that reach 15+ million elite tech professionals. Our new proprietary theCUBE AI Video Cloud is breaking ground in audience interaction, leveraging theCUBEai.com neural network to help technology companies make data-driven decisions and stay at the forefront of industry conversations.