 AI
AI
 AI
AI
 AI
AI
Graph database company Neo4j Inc. said today it’s embarking on a multiyear strategic collaboration with the cloud computing giant Amazon Web Services Inc. to enable enterprises to enhance the capabilities of their generative artificial intelligence models.
The idea is to combine knowledge graphs with native vector search in order to reduce the occurrence of so-called “hallucinations,” while ensuring models become more accurate, transparent and explainable. The partnership will also solve headaches around the need for long-term memory for large language models trained on specific enterprise datasets.
Together with the collaboration, Neo4j is launching Neo4j Aura Professional, its fully managed graph database platform, in the AWS Marketplace. Generally available starting today, it will enable companies to get started with the Neo4j database much more rapidly, the company said.
Neo4j’s platform is different from traditional database platforms. Rather than storing data in tables that consist of rows and columns, it relies on graph structures made up of nodes, edges and properties to represent and store information. The advantage of this format is that data retrieval is much easier, and can be done in a single operation in most cases.
One of the biggest advantages of Neo4j is its native vector search capabilities, which allow unstructured information such as images and written notes to be stored as vector embeddings that capture both explicit and implicit relationships and patterns. Using these systems, AI can retrieve and harness a much wider variety of data to enhance its ability to reason and infer.
Neo4j says these capabilities make its database ideal for grounding LLMs, while at the same time acting as a long-term memory store to enable more accurate, explainable and transparent outcomes for generative AI systems.
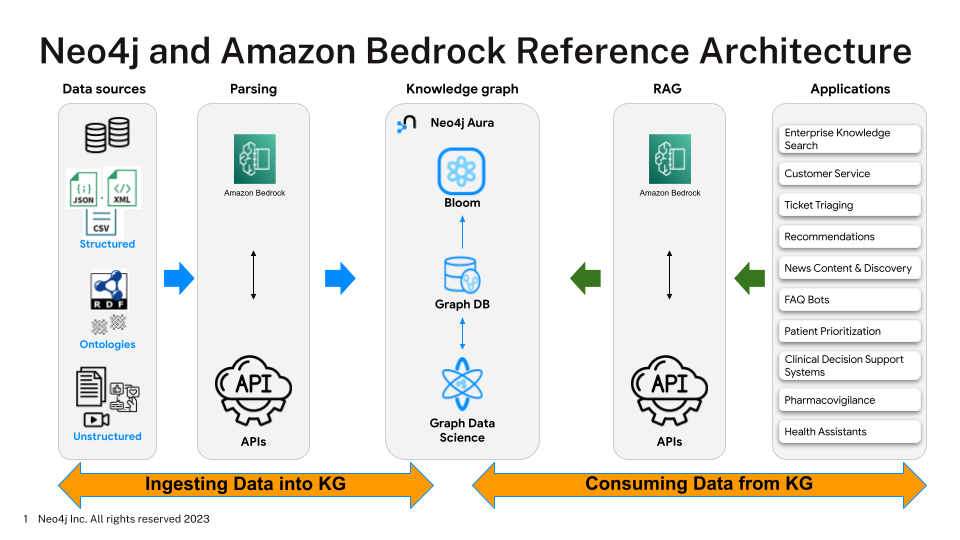
As part of the collaboration with AWS, Neo4j is integrating its platform with Amazon Bedrock, which is a fully managed service that makes foundational LLMs from third-parties accessible to AWS users. It has also created a reference architecture (pictured) that joint customers can use to access a catalog of models via application programming interfaces and use them as the foundation for AI applications.
Some of the benefits claimed by the company include a reduction in hallucinations, which is when AI fabricates its responses. Companies can use a technique called Retrieval Augmented Generation, where LLMs can tap into their proprietary data to create virtual assistants grounded in enterprise knowledge. They’ll also be able to create more personalized experiences and deliver more complete answers by leveraging real-time search so their models are always up to date.
Finally, the company said customers will now be able to leverage their unstructured data, processing it so that it becomes structured through its knowledge graphs and vector embeddings. Once this data is safely stored in a knowledge graph, AI models can tap into it for training and inference purposes.
“With Neo4j’s graph database and Amazon Bedrock’s integration, we aim to provide customers sophisticated options to deliver more accurate, transparent, and personalized experiences for their end-users in a fully managed manner,” said Amazon Bedrock General Manager Atul Deo.
Support our mission to keep content open and free by engaging with theCUBE community. Join theCUBE’s Alumni Trust Network, where technology leaders connect, share intelligence and create opportunities.
Founded by tech visionaries John Furrier and Dave Vellante, SiliconANGLE Media has built a dynamic ecosystem of industry-leading digital media brands that reach 15+ million elite tech professionals. Our new proprietary theCUBE AI Video Cloud is breaking ground in audience interaction, leveraging theCUBEai.com neural network to help technology companies make data-driven decisions and stay at the forefront of industry conversations.