 AI
AI
 AI
AI
 AI
AI
With Sanjeev Mohan, Tony Baer, Carl Olofson, Dave Menninger and Doug Henschen
In the words of famous people such as Nobel laureate Neils Bohr and baseball legend Yogi Berra, predictions are very difficult, especially if they’re about the future.
In this special Breaking Analysis, we’re pleased to host our third annual data predictions power panel with some of our collaborators in theCUBE Collective and members of the data gang. With us today are five of the top industry analysts focused on data platforms. Sanjeev Mohan of Sanjmo, Tony Baer of dbInsight, IDC’s Carl Olofson, Dave Menninger of Ventana Research, now part of ISG, and Doug Henschen with Constellation Research.
Before we get into it, let’s share some data from Enterprise Technology Research’s October survey of more than 1,700 information technology decision makers.
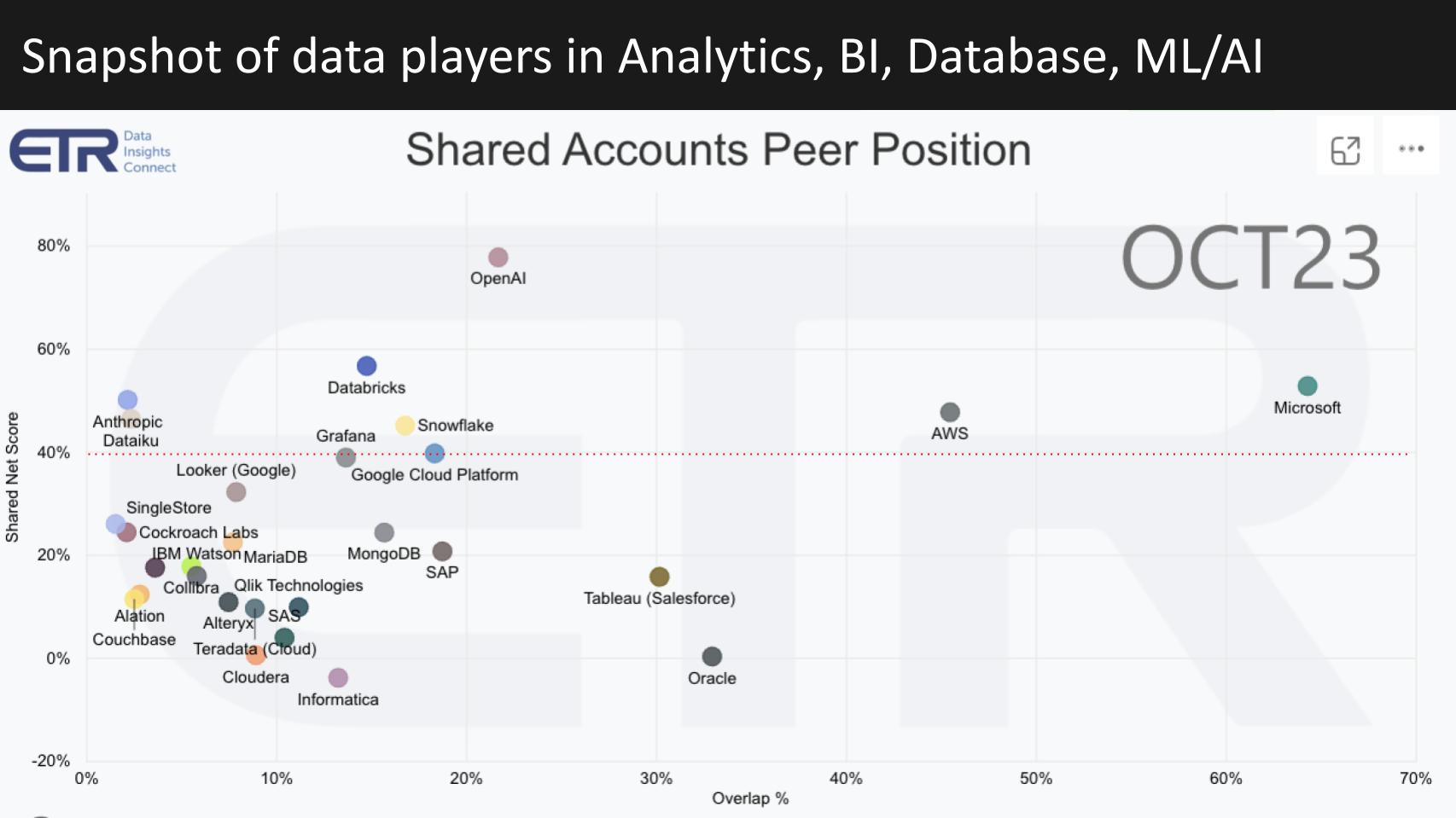
This graphic shows Net Score or spending momentum on the vertical axis and the Overlap of these platforms within those 1,700 accounts, representing their pervasiveness within the data set. This data is specifically for the analytics, business intelligence, database/data warehouse and machine learning/artificial intelligence sectors. We’ve chosen a subset of the companies in this group of sectors that are representative of leading vendors, many included in today’s discussion. That red line at 40% indicates highly elevated spending velocity on a platform.
A couple of quick points include: 1) the presence of Microsoft Corp. and Amazon Web Services Inc. in these combined sectors is notable and well ahead of Google Cloud; 2) the momentum of OpenAI, at a Net Score of nearly 80%, is astoundingly impressive and its presence on the X axis represents about seven times the account penetration of Anthropic PBC, which you see on the lefthand side of this chart just above Dataiku Inc.; 3) Snowflake Inc. and Databricks Inc. remain above the 40% mark with strong momentum and 4) you can see a number of companies that we’ll discuss directly and indirectly across this graphic in the basket of sectors, including MongoDB Inc., SAP SE, IBM Watson, as well as governance, metadata, pipeline and extract/transform/load tools such as Informatica Inc., Collibra NV, Alation Inc., Alteryx Inc. and others. There are also business intelligence platforms such as Thoughtspot Inc., QlikTech International AB, Tableau and Looker, and of course a number of database and data analytic platforms such as Couchbase Inc., Cloudera Inc., SAS Institute Inc. and notably Oracle Corp. and SAP.
This gives you a general quantitative sense of the relative position of these platforms in what is a multihundred billion-dollar total available market.
Let’s get started by looking back at our 2023 predictions and looking at how the analysts fared.
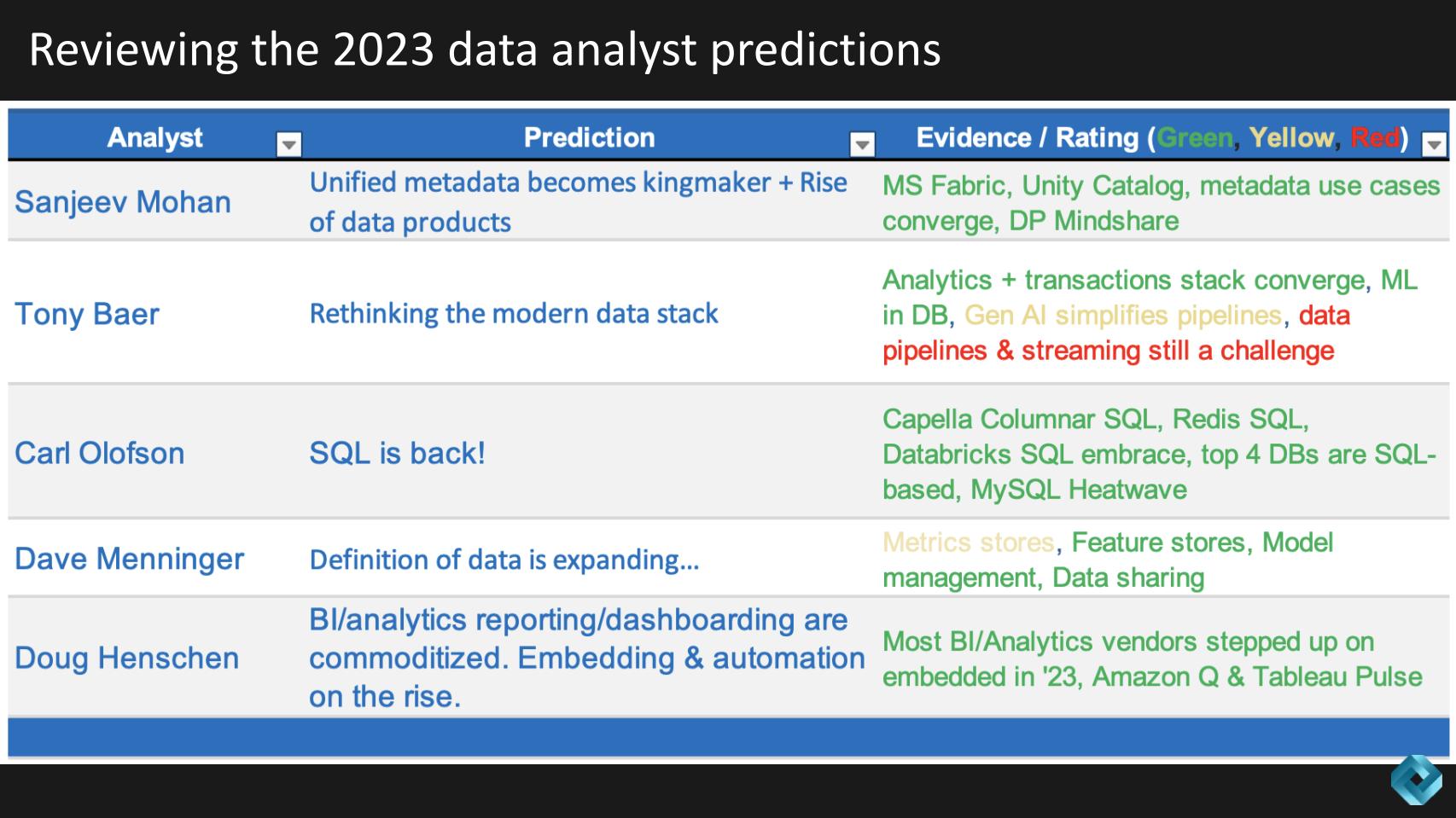
The graphic below shows all of the 2023 predictions for each analyst in one table with some commentary on evidence of whether the prediction was a direct hit (green), a glancing blow (yellow) or a miss (red). So a quick scan of the heat map shows you the data gang did pretty well – notwithstanding these were self-evaluated by each analyst.
Let’s get into each of the 2023 predictions starting with Sanjeev Mohan.
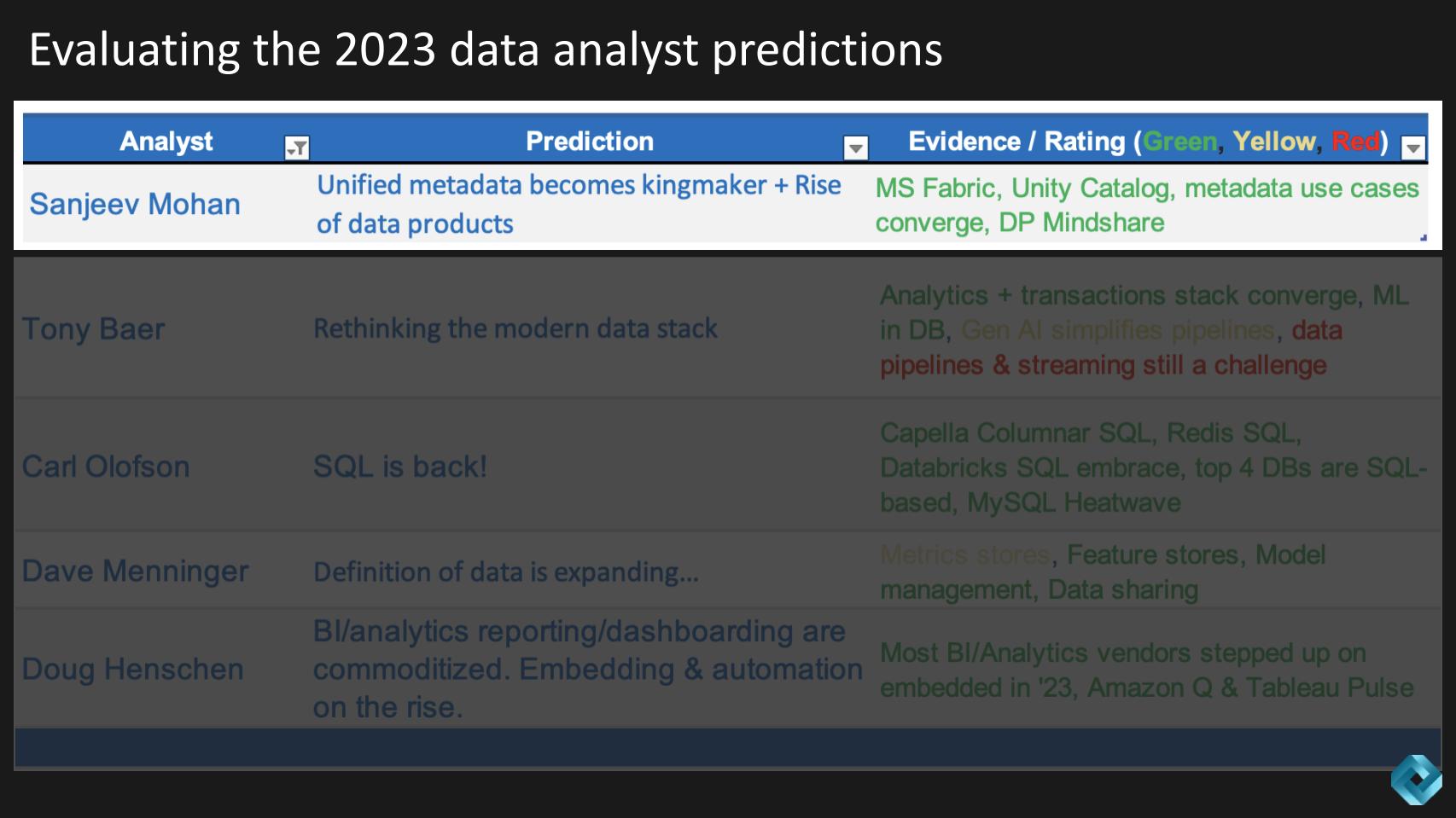
Above we show Sanjeev’s predictions about unified metadata becoming the kingmaker and his expectation that data products would rise in popularity. Sanjeev cites as evidence Microsoft Fabric, Databricks Unity Catalog and some other proof points. We further summarize Mohan’s predictions as follows:
Reflecting on the previous year’s predictions, it’s evident that the expectations around data catalogs and data products were not only met but exceeded, particularly in the context of AI’s rapid advancements. The transformation of data catalogs into multifaceted tools and the mainstreaming of data products highlight significant progress in these areas.
Data catalogs and data products have not only met the expectations set last year but have also significantly evolved, especially in light of AI’s growing influence. Data catalogs are now more than mere repositories, playing pivotal roles in various aspects of data management. Similarly, data products have transitioned from niche concepts to mainstream tools integral to data strategies, with their scope and application continuously expanding. This progress indicates a positive trend toward more integrated, AI-enhanced data management solutions.
Watch and listen to Sanjeev Mohan’s review of his 2023 predictions.
Next we go to Tony Baer, who predicted that the industry would begin to rethink the modern data stack. He cites some evidence of that with a mix of green, yellow and red.
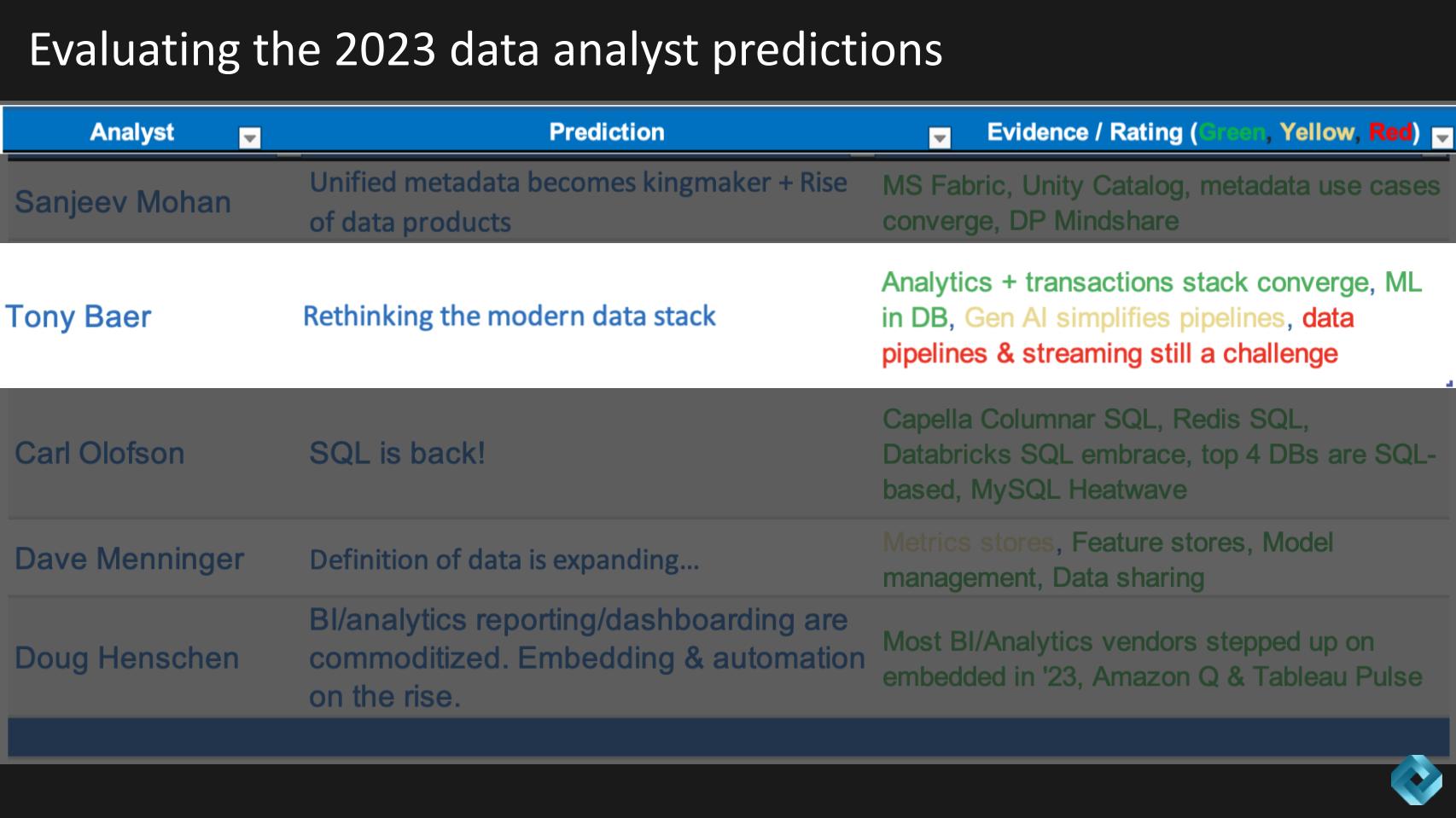
Tony further defended his and we summarize his thoughts below.
Mohan’s analysis of the modern data stack’s performance in the past year reveals a mixed picture of progress and challenges. The concept, aimed at modularizing the transition from transactional to analytic data, brought significant advancements in some areas but also introduced complexities.
While the modern data stack has achieved impressive advancements in certain areas like database integration and machine learning, it still faces hurdles in simplifying complexities and seamlessly integrating various tools. The evolving landscape suggests a potential role for generative AI in addressing these challenges, particularly in data pipeline management.
Watch and listen to Tony Baer’s review of his 2023 predictions.
OK, moving right along, Carl Olofson predicted that in 2023, SQL will be back! And he shows a sea of green in his evidence column. We asked Carl, “Was SQL ever gone?”
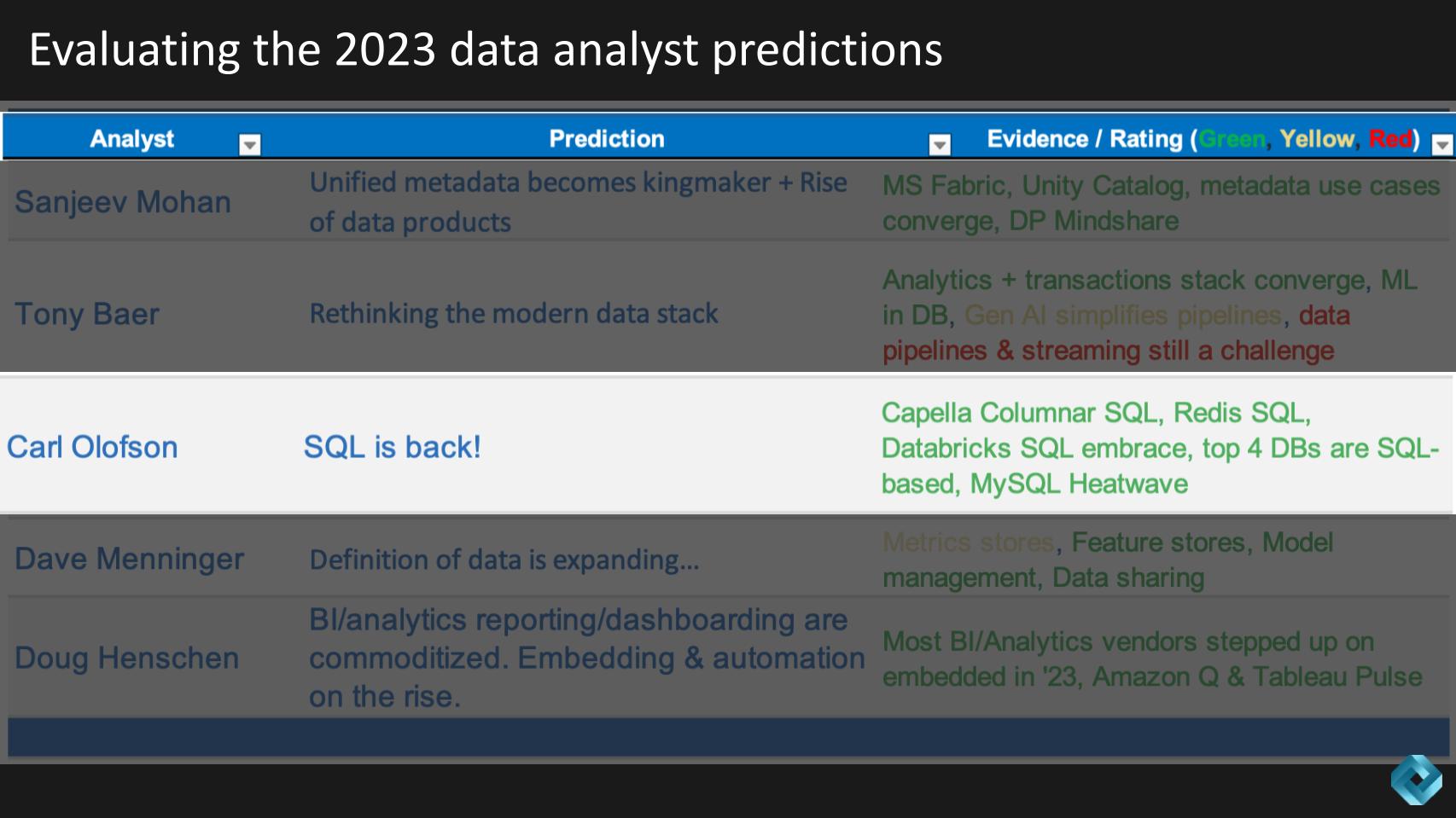
Here’s how we summarize Carl’s 2023 prediction and the related proof points that led to the direct hit evaluation.
In contrast to earlier predictions made by some about SQL’s demise, the past year has demonstrated not only its resilience but also its growing relevance in the data management landscape. Despite initial claims of its obsolescence, major players in the database industry have increasingly embraced SQL, underscoring its enduring importance.
Far from becoming obsolete, SQL has experienced a resurgence, with major database companies increasingly integrating it into their platforms. The data management industry is evolving toward a multimodel future, where SQL’s versatility in data analysis continues to be invaluable. This trend supports our thesis that SQL will maintain its prominence as a primary tool for business data analysis, despite the growing diversity in database technologies and formats.
Take a look at Carl Olofson’s review of his 2023 prediction.
David Menninger predicted that the definition of data is expanding, using metric stores, features stores, model management and data sharing as examples of what we could expect. His self-evaluation shows a mostly green level of accuracy for his prediction.
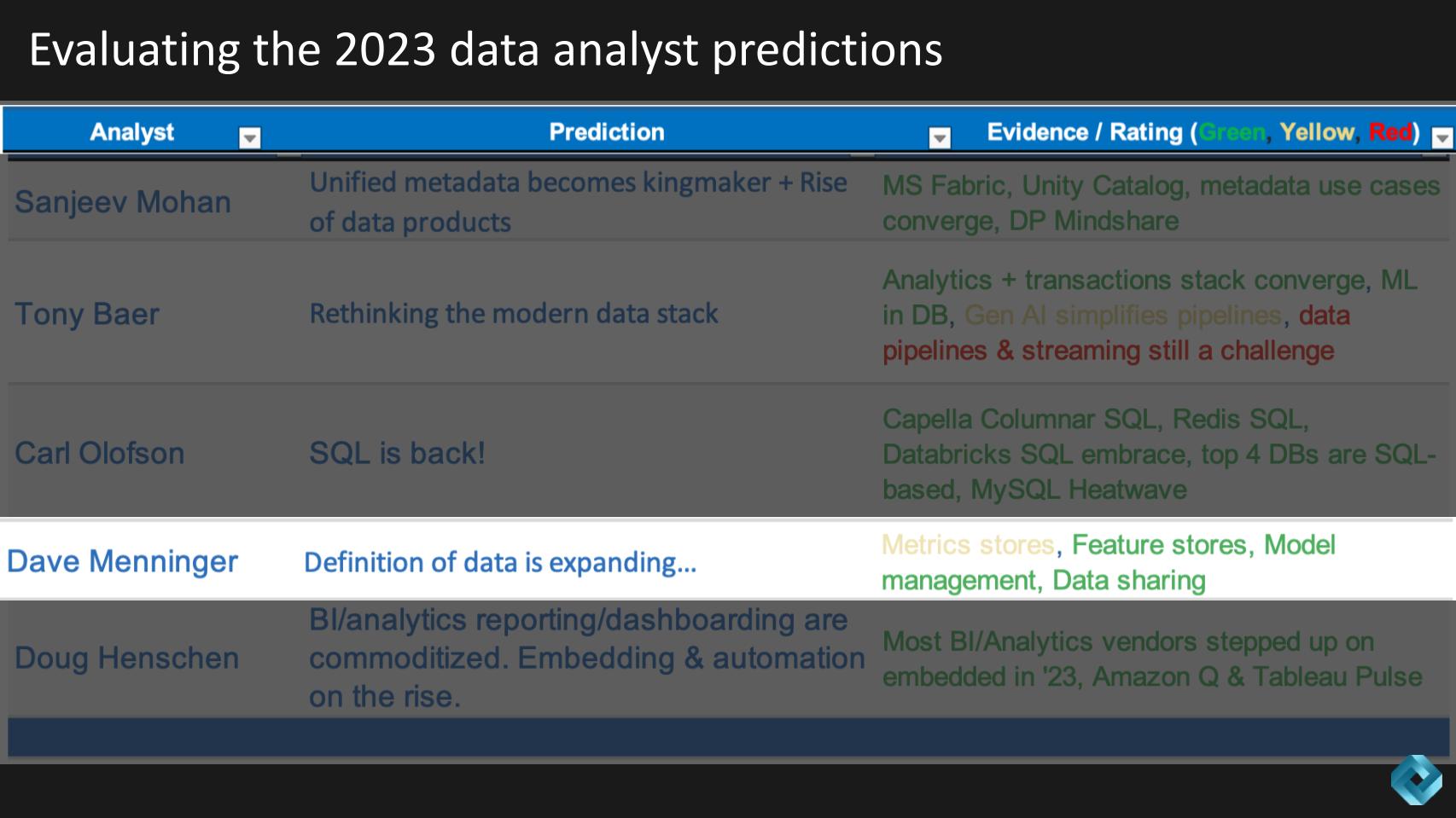
Menninger provides the following additional detail and we summarized as follows:
The past year has seen a significant expansion in the definition of data, largely influenced by the advent and integration of generative AI. Menninger notes that there is some degree of red in all the analysts’ look-back predictions because generative AI was not emphasized nearly to the degree the market has witnessed. Regardless, this shift has sparked increased attention in various AI-related processes and concepts, though some areas like metrics stores have received comparatively less focus.
The impact of gen AI on the data landscape is evident, with notable progress in AI-related processes and data sharing standards. However, areas like metrics stores and the comprehensive integration of AI processes into data catalogs have not received as much attention or development as anticipated. This mixed progress highlights the dynamic nature of the data industry, where certain trends gain prominence while others await further exploration and investment.
Watch Dave Menninger review his 2023 predictions.
Last but not least for the 2023 look-back, Doug Henschen forecast last year that BI analytics reporting and dashboarding would be commoditized; and that embedding and automation would ascend. He shared some examples below of evidence for his all green evaluation.
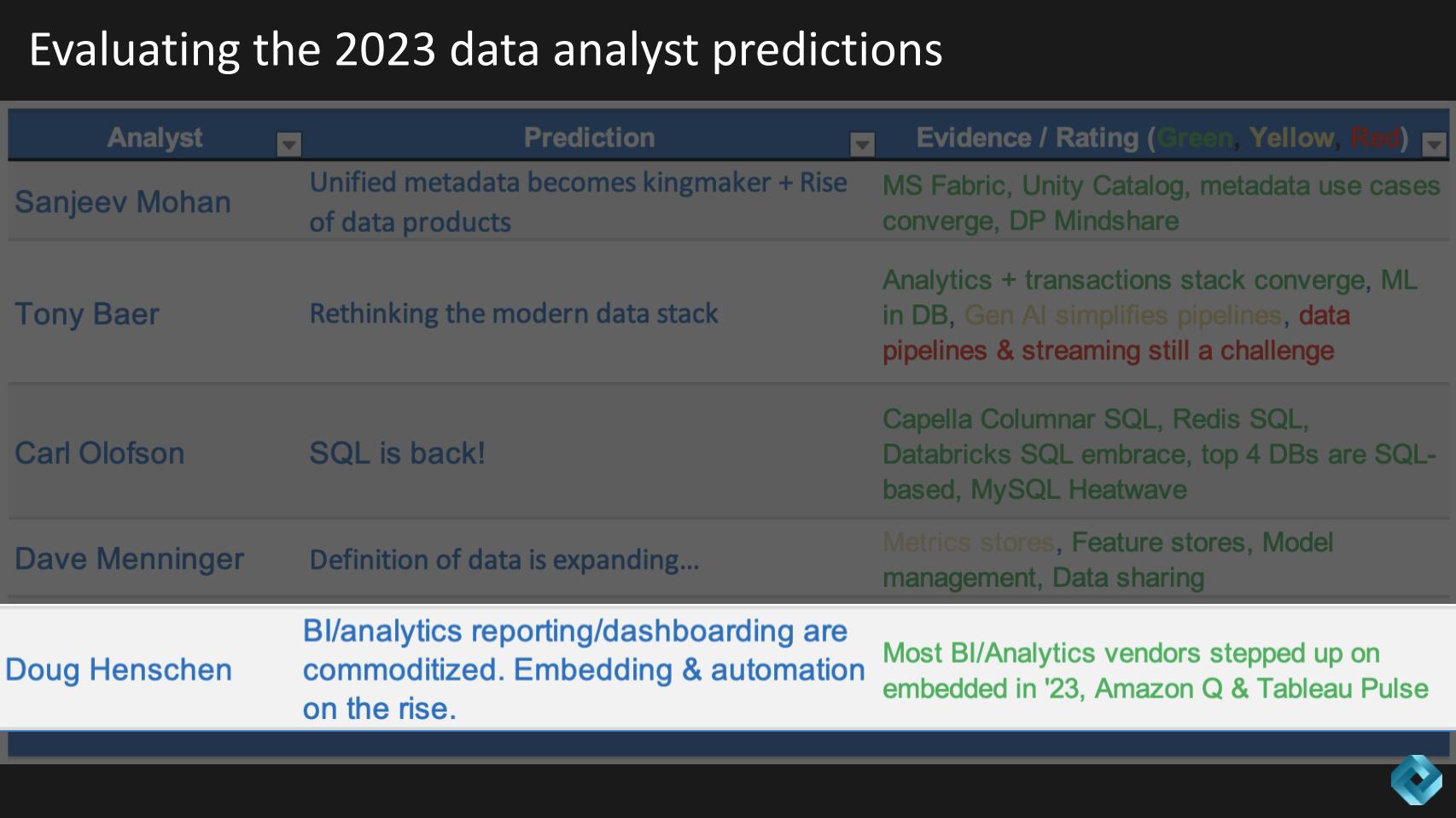
Our summary of Henschen’s rationale is below.
In 2023, the trend of embedded BI and analytics continued its upward trajectory, aligning with previous predictions. This year’s progress focused on integrating insights directly into decision-making processes within applications, rather than relying on separate reports and dashboards.
Embedded BI and analytics have seen significant strides in 2023, with a clear focus on making data-driven insights more accessible and actionable within the workflow of enterprise applications. The development of new tools and the integration of analytics into widely used enterprise platforms suggest a continuing trend toward more seamless, efficient and user-friendly data analysis methods in the business environment. This trend is poised to evolve further in 2024, with upcoming advancements in natural language processing and AI integration.
Watch Doug Henschen’s review of his 2023 predictions.
Keeping the same analyst order, the designated analyst presents his prediction and we made time to have one or two other analysts chime in on the prediction.
Below we show a table of all the predictions for 2024. All of them have AI included, but the forecasts span new data platforms, governance, metadata, database, skills gaps and more, so let’s get into it.
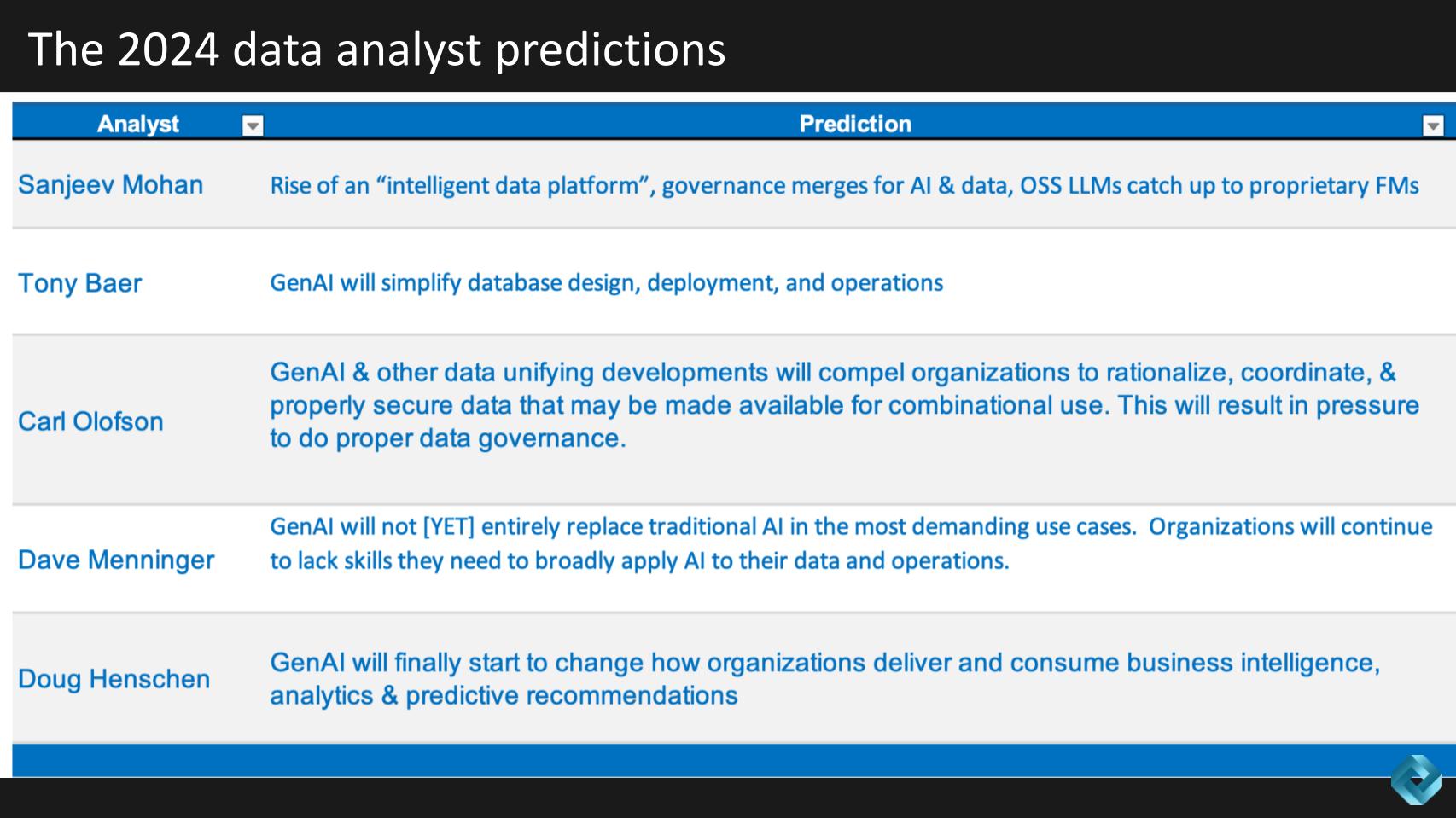
Sanjeev Mohan predicts the emergence of a new data platform, the convergence of governance for AI and data and open-source LLMs catching up to proprietary foundation models. On Breaking Analysis, we’ve been talking about a next data platform beyond the so-called modern data platforms of Snowflake, Databricks, Google, AWS, Microsoft — and let’s include Oracle in that mix, as it is the king of databases.
Sanjeev had a lot to cover and we summarize his prediction below with a reaction from Doug Henschen and Dave Menninger.
Mohan’s primary prediction for 2024 is the emergence and adoption of the “intelligent data platform,” which represents a significant advancement in integrating AI into existing data stacks. This concept focuses on minimizing data movement and integrating various components, including AI models and analytical engines, into a unified platform and aligns with theCUBE Research work around the so-called sixth data platform.
The intelligent data platform is envisioned as a comprehensive, integrated system that combines data management and AI capabilities. This platform is expected to streamline processes, enhance analytics, and provide a more cohesive governance structure for both data and AI models.
Doug Henschen and Dave Menninger responded to the prediction with a mix of appreciation for its ambition and caution about its immediate feasibility.
Overall, while acknowledging the innovative potential of the intelligent data platform, analysts caution against overestimating current market readiness and emphasize the gradual nature of such a significant technological shift.
Watch and listen to Sanjeev’s prediction and the analysts’ reaction to his 2024 forecast.
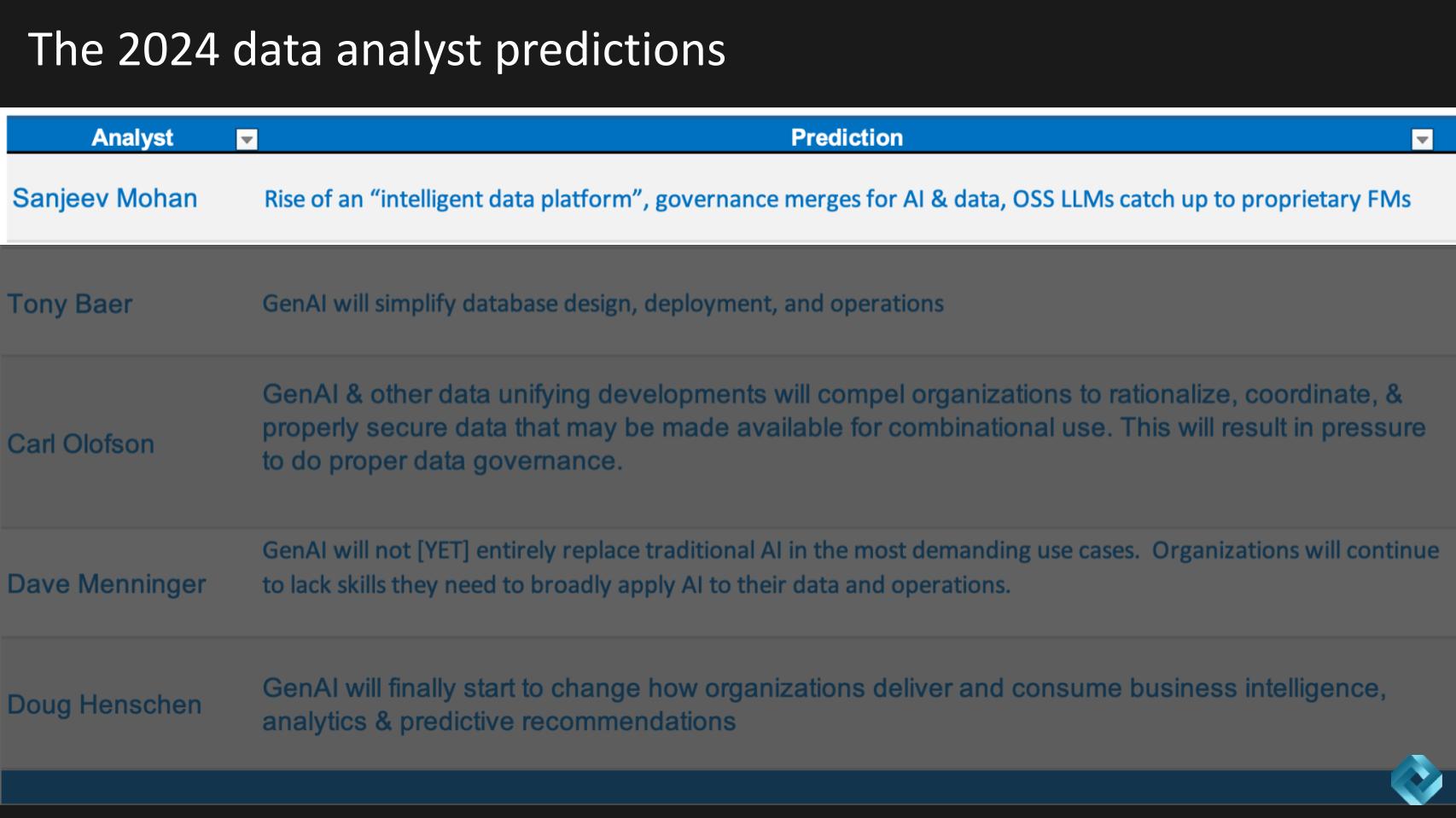
Tony Baer predicts that gen AI will make things simpler for database practitioners.
We asked him to explain how so and we summarize his response below.
Tony’s prediction for 2024 focuses on the deeper integration of generative AI and machine learning into database operations, transforming how databases are managed and interacted with. This integration is expected to bring more subtle, yet incremental improvements rather than drastic changes, enhancing automation and efficiency in database design and management.
Gen AI and machine learning are poised to further permeate database operations, offering more sophisticated, automated and efficient ways to handle complex data tasks. This trend represents a shift toward simplifying interactions with complex data systems through intelligent technology.
Carl Olofson’s response added the following to the prediction. He affirms its potential while emphasizing its synergistic relationship with broader data management trends.
Olofson generally agrees with the prediction, seeing it as a realistic and practical evolution of database management that aligns well with the broader movement toward intelligent and automated data platforms.
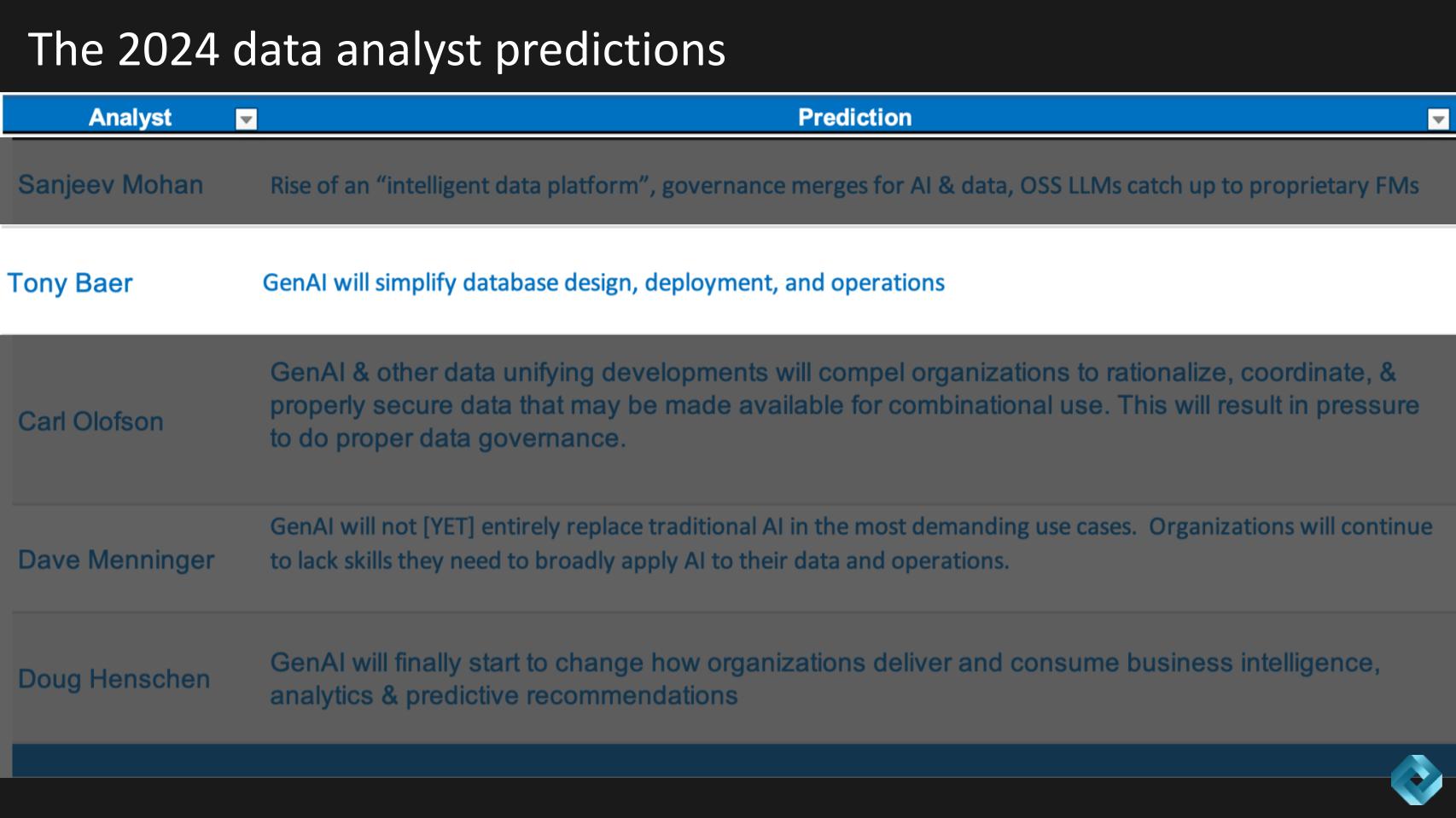
Carl Olofson’s 2024 prediction is shown below. He predicts that gen AI and other developments will catalyze a rationalization of data silos to enable combinatorial data use cases which will ultimately create governance challenges. So while some may see this as obvious, we asked if Carl is predicting organizations will be able to succeed in 2024, or will this governance challenge create insurmountable barriers to positive outcomes?
Olofson provided the following additional color to his prediction and we summarize below as follows:
Carl’s prediction for 2024 delves into the complexities of data organization within enterprises, particularly in the context of generative AI. It emphasizes the current disarray in enterprise data ecosystems and the potential challenges that will arise as generative AI begins to combine data in unprecedented ways.
The integration of generative AI in enterprise data systems is not a simple add-on; it requires a fundamental reassessment and restructuring of how data is organized and managed. This process is expected to be complex and time-consuming, necessitating careful planning and execution.
Tony Baer and Doug Henschen react to this prediction by acknowledging the inherent complexities and echo the concerns about integrating generative AI into chaotic data environments.
The analysts generally agree with the prediction, highlighting the challenges in harmonizing heterogeneous data environments and the need for adaptable, multifaceted data management approaches.
Watch Carl Olofson’s 2024 prediction and the analysts’ reaction to his call.
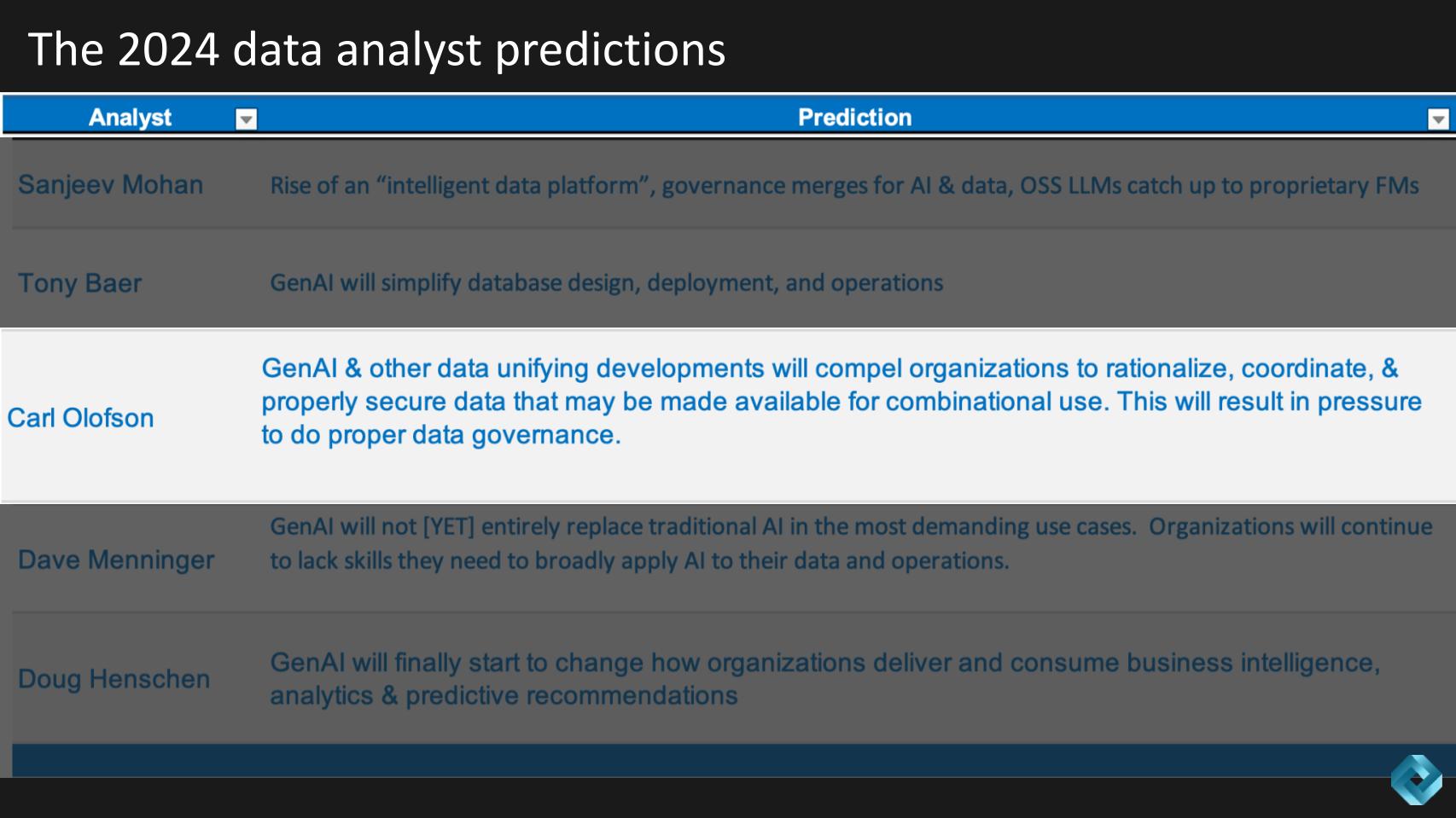
Dave Menninger predicts that despite all the hype around gen AI, it won’t replace traditional AI in the most demanding use cases. He predicts a continued AI skills gap. This is another prediction that feels like a lock, so we asked Dave to add some data points to increase the degree of difficulty for this call.
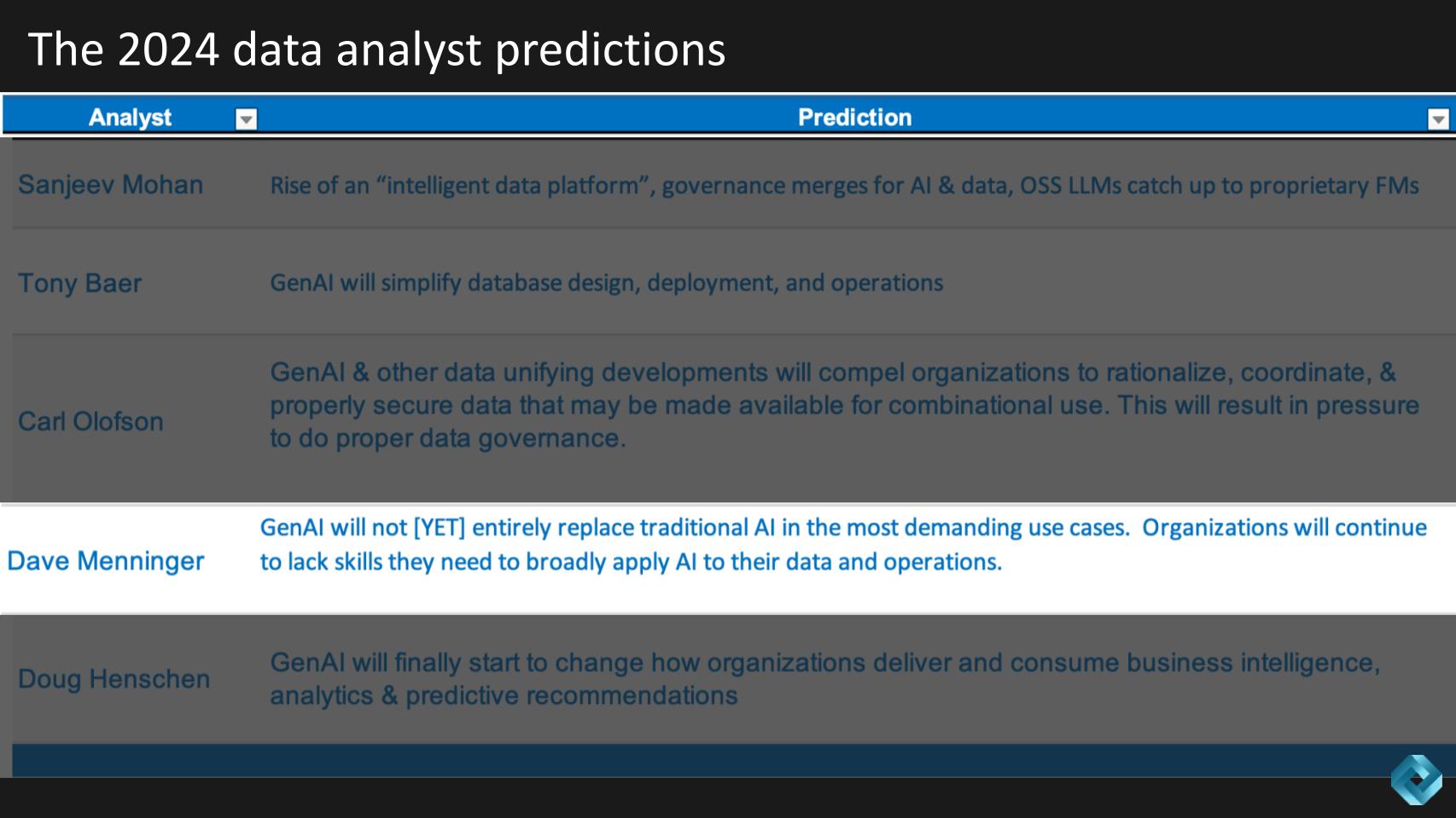
We summarize his response as follows:
Dave’s prediction for 2024 highlights the limitations of gen AI in demanding use cases, despite its rapid advancements and growing popularity. It emphasizes the need for a balanced approach in adopting gen AI, acknowledging its strengths in certain areas while recognizing its current limitations in more complex, specialized fields.
Though generative AI presents exciting advancements, it’s important to recognize its limitations and not overly depend on it for complex and critical tasks. A balanced approach, valuing both gen AI and traditional AI skills, is crucial for effective and responsible AI adoption.
Sanjeev Mohan and Carl Olofson responded with analysis that underscores the limitations of gen AI and advocates for a balance between technological advancement and skilled human intervention.
The analysts concur that though gen AI is a significant development, it is not a panacea for all challenges. Skilled human oversight remains essential, especially in sophisticated and nuanced applications.
Watch Dave Menninger’s 2024 prediction and the analysts’ response to his call.
The last prediction comes from Doug Henschen, who is predicting that gen AI will have a material impact on how organizations approach BI and predictive analytics. Doug’s prediction has big implications for data analysts, data pros working in the pipeline, Tableau jocks and business end-users. We wanted to know from Doug if he’s predicting that we’ll see a measurable transformation before the end of the year.
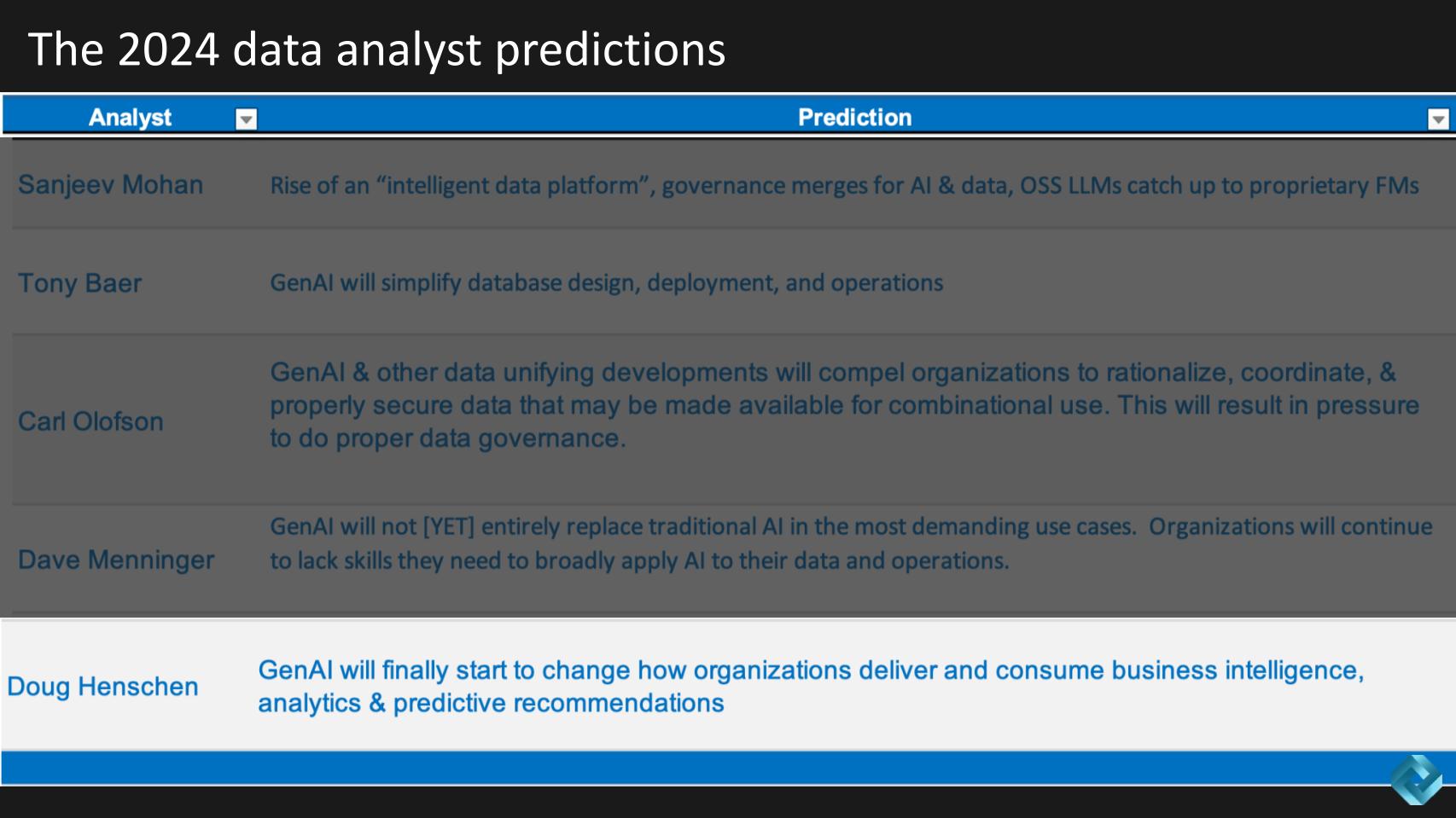
Henschen provided additional details about this prediction and we summarize his analysis below.
The prediction for 2024 is a continuation of the 2023 trend, focusing on the increasing integration of insights and natural language queries within BI analytics. This trend is particularly characterized by the augmentation of natural language query capabilities, fueled by advancements in generative AI.
The integration of generative AI into BI analytics is poised to revolutionize how insights are accessed and interacted with, enhancing the natural language querying experience and embedding these capabilities across various applications.
Dave Menninger, Tony Baer and Sanjeev Mohan had reactions that underscore the potential of this trend in democratizing access to analytics and shifting the role of analysts.
The analysts generally agree with the prediction, highlighting the transformative potential of generative AI in making analytics more accessible and shifting the focus of analysts toward more nuanced aspects of data interaction.
What do you think of our 2023 data predictions, the assessment of their accuracy by the analysts and the relevance of our 2024 predictions? Let us know and thanks for reading!
Thanks to Alex Myerson and Ken Shifman on production, podcasts and media workflows for Breaking Analysis. Special thanks to Kristen Martin and Cheryl Knight ,who help us keep our community informed and get the word out, and to Rob Hof, our editor in chief at SiliconANGLE.
Remember we publish each week on Wikibon and SiliconANGLE. These episodes are all available as podcasts wherever you listen.
Email david.vellante@siliconangle.com, DM @dvellante on Twitter and comment on our LinkedIn posts.
Also, check out this ETR Tutorial we created, which explains the spending methodology in more detail. Note: ETR is a separate company from theCUBE Research and SiliconANGLE. If you would like to cite or republish any of the company’s data, or inquire about its services, please contact ETR at legal@etr.ai or research@siliconangle.com.
Here’s the full video analysis:
All statements made regarding companies or securities are strictly beliefs, points of view and opinions held by SiliconANGLE Media, Enterprise Technology Research, other guests on theCUBE and guest writers. Such statements are not recommendations by these individuals to buy, sell or hold any security. The content presented does not constitute investment advice and should not be used as the basis for any investment decision. You and only you are responsible for your investment decisions.
Disclosure: Many of the companies cited in Breaking Analysis are sponsors of theCUBE and/or clients of Wikibon. None of these firms or other companies have any editorial control over or advanced viewing of what’s published in Breaking Analysis.
Support our mission to keep content open and free by engaging with theCUBE community. Join theCUBE’s Alumni Trust Network, where technology leaders connect, share intelligence and create opportunities.
Founded by tech visionaries John Furrier and Dave Vellante, SiliconANGLE Media has built a dynamic ecosystem of industry-leading digital media brands that reach 15+ million elite tech professionals. Our new proprietary theCUBE AI Video Cloud is breaking ground in audience interaction, leveraging theCUBEai.com neural network to help technology companies make data-driven decisions and stay at the forefront of industry conversations.