 SECURITY
SECURITY
 SECURITY
SECURITY
 SECURITY
SECURITY
A new report into so-called “initial access brokers” from threat intelligence firm Kela Research and Strategy Ltd. has detailed some disturbing trends in the criminal internet underworld and those involved in ransomware endeavors.
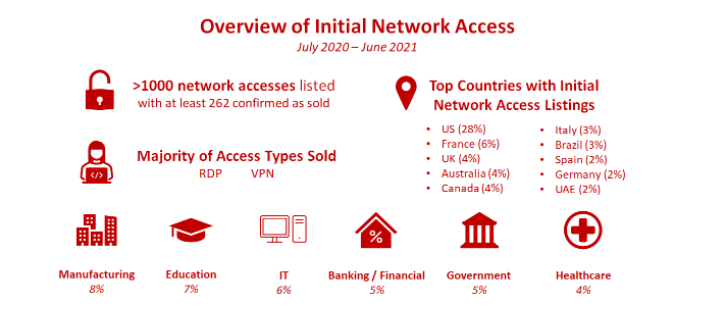
The Kela report was based on exploring over 1,000 access listings over the last year. IABs are threat actors who sell access to malicious services and play a crucial role in the ransomware-as-a-service economy. IABs facilitate network intrusions by selling remote access to a computer in a compromised organization and link opportunistic campaigns with targeted attacks, often ransomware operators. IABs don’t undertake ransomware attacks but sell access to a compromised network that is then used by ransomware gangs and others.
In one example, the DarkSide ransomware gang published a post on Feb. 20 claiming that they had compromised Gyrodata Inc., a technology provider in the energy industry. A month before DarkSide claimed Gryodata as a victim, an IAB was observed selling access to the company with the access sold on Jan. 18. What this suggests is that DarkSide or a DarkSide affiliate obtained access to Gyrodata from the IAB.
It’s a similar tale to an attack on a UAE supplier of steel products. The Avaddom ransomware operators claimed to have breached the company on March 31, but and IAB had offered access to the same company at the beginning of March.
Money is a major motivator for IABs. The data in the report found that the average price being asked for network access during the period studied was $5,400 while the median price was $1,000. The top affected countries included the U.S., France, U.K., Australia, Canada, Italy, Brazil, Spain, Germany and the UAE.
Not all listings are created equally, however, with IABs using a pricing model for initial access. The most valuable offers include domain admin privileges on a computer within a company with hundreds of millions in revenue. Access to smaller companies with less opportunity for ransomware extortion attracted lower rates.
Remote Desktop Protocol and virtual private network-based access are the most common offers with attack vectors including network management and virtual servers also on offer.
Successful IABs are said to find regular customers, some of which are ransomware affiliates and move most of their operations private conversations. However, the report notes that new actors continually enter the scene.
Interestingly, some IABs were found to adopt ethics introduced by some ransomware gangs, such as not providing access to healthcare companies although they are still few and far between. This refers to a group of cybercriminals in March 2020 that was actively discouraging others to not profit from the COVID-19 pandemic.
Support our mission to keep content open and free by engaging with theCUBE community. Join theCUBE’s Alumni Trust Network, where technology leaders connect, share intelligence and create opportunities.
Founded by tech visionaries John Furrier and Dave Vellante, SiliconANGLE Media has built a dynamic ecosystem of industry-leading digital media brands that reach 15+ million elite tech professionals. Our new proprietary theCUBE AI Video Cloud is breaking ground in audience interaction, leveraging theCUBEai.com neural network to help technology companies make data-driven decisions and stay at the forefront of industry conversations.