 BIG DATA
BIG DATA
 BIG DATA
BIG DATA
 BIG DATA
BIG DATA
Neo4j Inc., maker of the most widely used graph database, today is releasing version 5 of its core engine to general availability, boasting major performance and scalability improvements.
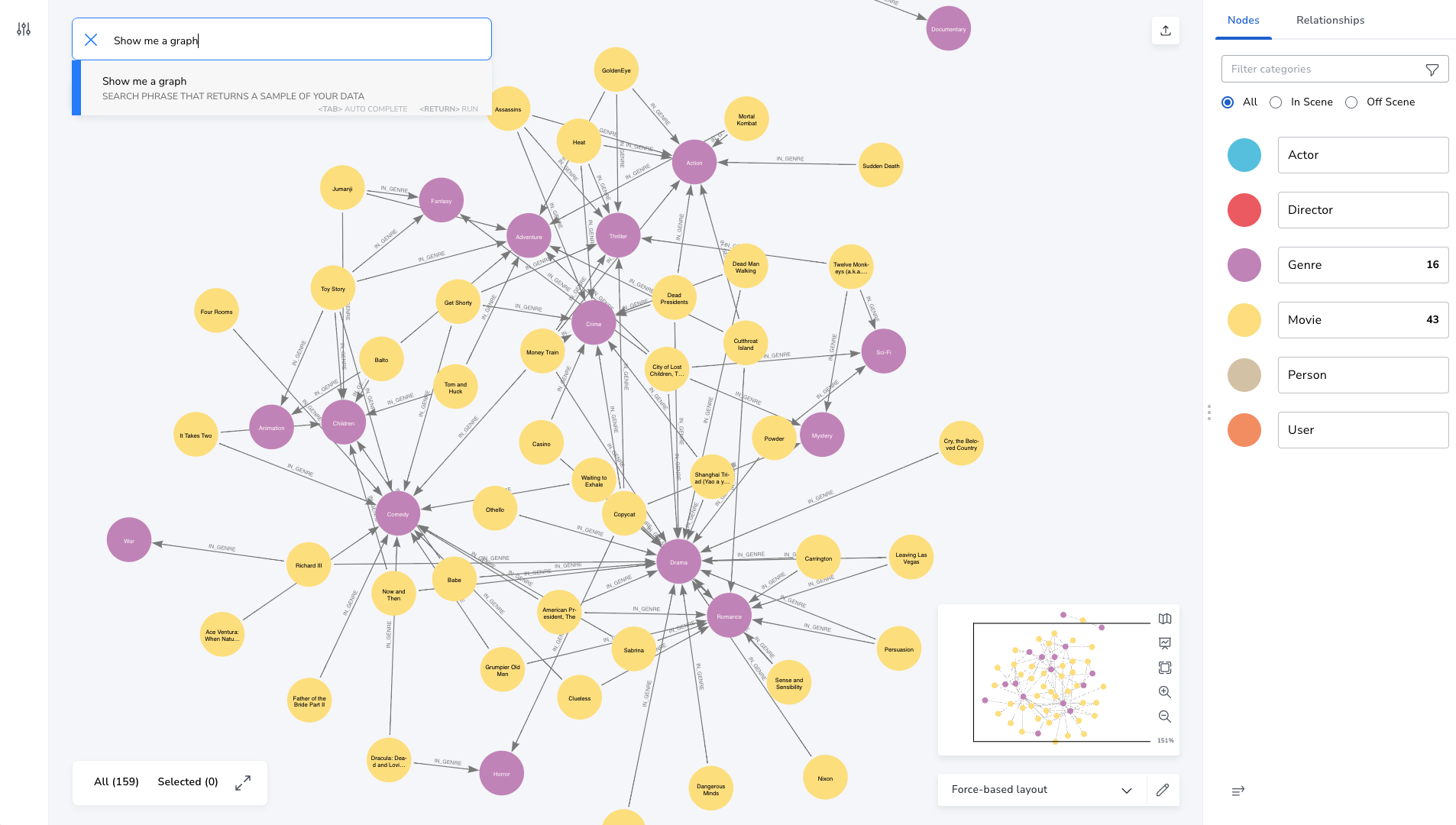
Graph databases have the unique ability to represent complex relationships in a way that enables rapid navigation between elements to discover correlations
The company’s AuraDB managed service has already been updated with the new release and self-managed customers can now download it. The most notable improvement is to the Cypher graph-native query language, which has been enhanced with more expressive constructs that make it easier for users to execute complex pattern-matching queries. Combined with improvements in indexes, query planning and runtime execution, multihop queries can now be executed between 50 and 1,000 times faster than in previous versions, said Ramanan Balakrishnan, senior director of product marketing at Neo4j.
The biggest performance gains are seen on K-hop queries, which search all nodes in a designated layer that are associated with the source node through a breadth-first search. This technique is commonly used in ranked keyword searches, social network analysis, fraud detection and supply chain optimization, Balakrishnan said. “It’s a deep query that involves a variable number of operations where you don’t know how far you have to go and you have calculations at every step,” he said. “The deeper the query goes, the faster it gets.”
Automated scale-out expansion across hundreds of machines is now supported, enabling self-managed customers to handle a larger number of queries with less manual effort and infrastructure cost. This is achieved with new and enhanced features like autonomous clustering and a fabric that automatically allocates and reassigns computing resources.
“Autonomous clustering helps you easily manage multiple databases within a cluster and optimizes on resource constraints and failures,” Balakrishnan said. “The fabric lets you take a really large graph, shard it and still query it as one single graph.”
Sharding is a database management technique that breaks up large databases into two or more smaller ones. “It’s like scaling your graph across multiple machines and clusters and seeing it as a single graph,” he said. “You can query across multiple business graphs so your marketing database and your supply chain database can be seen as a single database.”
Neo4j also said it will change the way it manages the distribution of updates to ensure compatibility between self-managed and AuraDB workloads. The managed service is updated roughly once a month but updates are distributed to on-premises customers twice a year. In the future, self-managed customers will receive updates more frequently with a guarantee that their graph-based applications will work both on-premises and in the cloud.
“Customers can choose to pause on new releases, wait for all the ‘dot releases’ to come out or adopt any version they want,” Balakrishnan said.
THANK YOU