 BIG DATA
BIG DATA
 BIG DATA
BIG DATA
 BIG DATA
BIG DATA
Graph database startup TigerGraph Inc. is coming out with version 2.0 of its platform today, offering what it says is a unique feature that enables multiple users to work on the same graph simultaneously.
Graph databases are a type of NoSQL database that represent data as objects rather than in rows and columns. Connections can be traversed quickly to find relationships that would require multiple resource-consuming joins using relational technology.
These databases are used for tasks involving large and complex relationships that must be visualized and navigated quickly, such as fraud detection and customer recommendation engines. Forrester Research Inc. recently estimated that just over half of data- and analytics-intensive organizations are using graph databases.
TigerGraph, which launched in September with $31 million in funding, claims to have the fastest engine of its kind on the market, along with the scalability to support multihop queries of up to trillions of relationships and to traverse more than 100 million edges per second.
The company said its real-time analytics capability is especially well-suited for fraud detection, a feature it has honed with the help of customer Alibaba Group Holding Ltd., which uses TigerGraph to process more than two billion real-time events per day. Alibaba’s Ant Financial venture capital arm is one of TigerGraph’s investors.
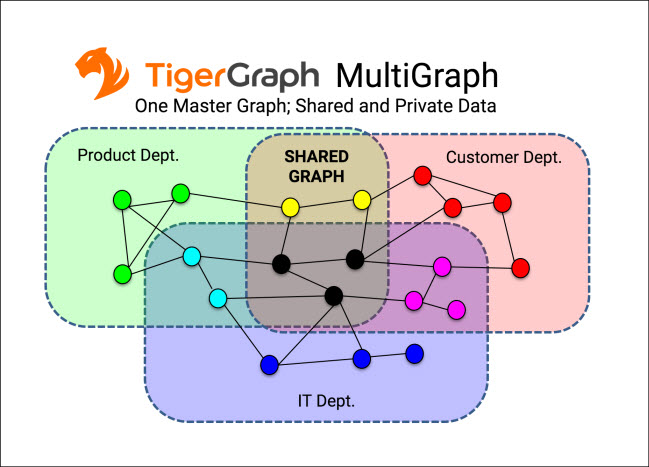
The new MultiGraph Feature gives organizations control over which parts of a graph or graphs users can access while maintaining security and data integrity. This enables several teams to use one database with multiple views.
“Traditionally, companies have had to copy or create a new database” every time another group wants access, said Todd Blaschka, the company’s chief operating officer. With MultiGraph, two groups can work on the same data set with one group retaining access to certain data that others can’t see or update, he said. Each group administrator controls what can be done with the database within its own domain, such as specifying write access privileges. Unlike a relational view, a multi-graph is a physical part of the database.
Security is handled at the query level, said Yu Xu, TigerGraph’s chief executive. “Before we pass a query through to the graph engine for execution, we do a semantic check,” he said. “If the query passes, it goes through. Even if it passes the semantic layer, queries can be blocked at the execution level.”
The graph schema is shareable across all departments, with each department able to see its own view of the schema, Xu added. However, all of the data is stored in the same system.
The new release also supports easier deployment across distributed platforms and improved security features that include single sign-on, support for directory services, role-based access control and encryption.
TigerGraph can be run both on-premises and in the cloud. Pricing is based upon the size of the graph database managed, but details were not disclosed.
Support our mission to keep content open and free by engaging with theCUBE community. Join theCUBE’s Alumni Trust Network, where technology leaders connect, share intelligence and create opportunities.
Founded by tech visionaries John Furrier and Dave Vellante, SiliconANGLE Media has built a dynamic ecosystem of industry-leading digital media brands that reach 15+ million elite tech professionals. Our new proprietary theCUBE AI Video Cloud is breaking ground in audience interaction, leveraging theCUBEai.com neural network to help technology companies make data-driven decisions and stay at the forefront of industry conversations.